Uterine Polyps: Expert Diagnosis & Safe Removal in Mumbai
Dr. Dimple Doshi (MBBS, MD, DGO)
Lady Gynecologist & Laparoscopic Surgeon
27+ years’ experience
20,000+ surgeries completed
Are You Facing Unexplained Bleeding or Fertility Issues?
- Do you experience irregular periods, spotting between cycles, or bleeding after intercourse?
- Are you feeling emotionally drained from failed pregnancy attempts or postmenopausal bleeding?
Such symptoms may point to uterine polyps—benign growths that silently disrupt menstrual health and fertility.
But here’s the good news: with advanced hysteroscopic treatment, these can be diagnosed and removed effectively—restoring hormonal balance, cycle regularity, and reproductive wellness.
According to ISAPS 2023, gynecological endoscopic procedures have increased by over 21% globally, with Indian women increasingly opting for safer, minimally invasive care.
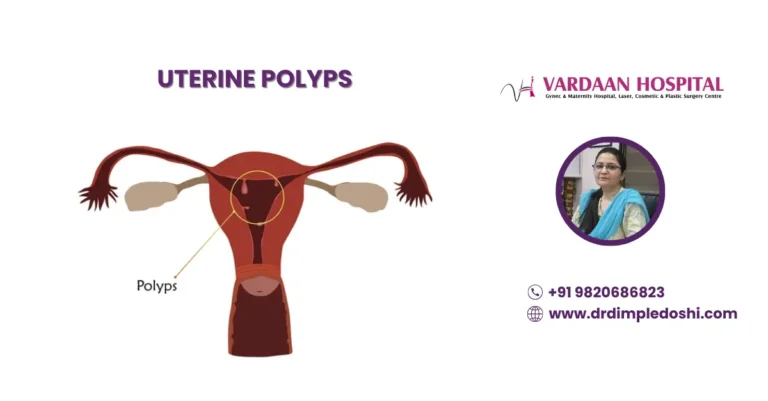
What Are Uterine Polyps and How Do They Affect You?
Uterine polyps are benign, hormone-sensitive overgrowths of the uterine lining that may cause bleeding or infertility.
- Also called: Endometrial or mucosal polyps
- Can cause spotting, heavy periods, or pregnancy issues
- Often diagnosed via ultrasound or hysteroscopy
What Causes Uterine Polyps?
Hormonal imbalance, especially excess estrogen, is the leading cause of uterine polyp formation.
- PCOS or anovulation
- Obesity and insulin resistance
- Perimenopausal estrogen shifts
- Use of tamoxifen (breast cancer medication)
- Chronic endometrial inflammation
What Are the Symptoms of Uterine Polyps?
Common symptoms include unusual menstrual bleeding, infertility, and vaginal discharge.
- Heavy or prolonged periods
- Spotting between cycles
- Bleeding after sex or post-menopause
- Foul-smelling discharge
- Difficulty conceiving or repeated miscarriages
How Are Uterine Polyps Diagnosed?
Diagnosis involves imaging, direct visualization, and biopsy to confirm benign or atypical growths.
- Transvaginal ultrasound (TVS)
- Saline infusion sonography (SIS)
- Hysteroscopy for diagnosis + removal
- Histopathology (biopsy)
What Are the Treatment Options for Uterine Polyps?
Hysteroscopic removal is the gold-standard treatment for symptomatic or suspicious polyps.
- Hormonal medications (temporary symptom relief)
- Hysteroscopic polypectomy (minimally invasive)
- Histopathology post-removal (to rule out cancer)
Can You Get Pregnant with Uterine Polyps?
Yes, but polyps near the uterine fundus or tubal opening may interfere with implantation.
- Polyps may reduce IVF success rates
- Timely removal improves conception chances
- Polypectomy may be recommended before fertility treatments
What Is the Cost of Uterine Polyp Treatment in Mumbai?
Hysteroscopic polypectomy costs in Mumbai range from ₹30,000–₹45,000 depending on the facility and complexity.
- Biopsy costs: ₹1,000–₹2,000
- Hormonal medications: ₹1,500–₹4,000/month
- Always consult your gynecologist for accurate estimates
Why Choose Dr. Dimple Doshi at Vardaan Hospital, Goregaon?
Dr. Dimple Doshi brings 25+ years of gynecological excellence, with special expertise in hysteroscopic procedures.
- Expert in hysteroscopic polypectomy with fertility focus
- Advanced technology like Karl Storz 3D systems
- Trusted by thousands of women across Mumbai
Medical Codes for Uterine Polyps
ICD-10 Codes for Uterine Polyps
| ICD-10 Code | Description |
|---|---|
| N84.0 | Polyp of corpus uteri (endometrial polyp) |
| N84.1 | Polyp of cervix uteri |
| N84.8 | Other specified polyp of female genital tract |
| N84.9 | Polyp of female genital tract, unspecified |
CPT Codes for Uterine Polyp Evaluation & Treatment
| CPT Code | Description |
|---|---|
| 58100 | Endometrial biopsy (for diagnosis of uterine polyps) |
| 58555 | Hysteroscopy, diagnostic (to visualize uterine cavity) |
| 58558 | Hysteroscopy, surgical; with removal of leiomyomata or polyps |
| 58120 | Dilation and curettage (D&C), diagnostic and/or therapeutic |
| 58145 | Myomectomy, removal of uterine fibroid (if associated with polyps) |
| 58563 | Hysteroscopic endometrial ablation (for recurrent polyps or abnormal bleeding) |
FAQs – Uterine Polyps
Q1. Can uterine polyps go away on their own?
Ans. Small, asymptomatic polyps may regress, but symptomatic or postmenopausal polyps need removal.
Q2. How are uterine polyps removed?
Ans. The gold-standard is hysteroscopic removal under visual guidance for complete excision and biopsy.
Q3. Are polyps painful?
Ans. Most polyps are painless, but larger ones may cause cramps, spotting, or bleeding after intercourse.
Q4. Can polyps be removed naturally?
Ans. No proven natural remedy exists; hormonal therapy may help symptoms but not remove the polyp.
Q5. What foods shrink polyps?
Ans. A fiber-rich, low-estrogen diet (cruciferous vegetables, flaxseeds) may support hormonal balance.
Q6. Can uterine polyps cause weight gain?
Ans. Polyps don’t cause weight gain directly but share hormonal roots with conditions like PCOS or obesity.
Q7. What is the cost of polyp removal in India?
Ans. ₹30,000 to ₹45,000 for hysteroscopic removal; biopsy and medications add ₹1,000–₹4,000 more.
Q8. Do polyps grow back?
Ans. They may recur, especially if underlying hormonal imbalance (e.g., estrogen dominance) isn’t corrected.
Q9. Will bleeding stop after removal?
Ans. Yes, most women notice relief from abnormal bleeding within one cycle post-polypectomy.
Q10. Are polyps dangerous?
Ans. While most are benign, atypical or postmenopausal polyps must be tested to rule out malignancy.
Q11. Can you see polyps on ultrasound?
Ans. Yes, especially transvaginal ultrasound or saline infusion sonography can detect polyps clearly.
Q12. Is polypectomy painful?
Ans. No, it is a short day-care procedure under anesthesia with quick recovery.
Q13. Can polyps be removed during pregnancy?
Ans. It depends—only large or bleeding polyps are considered for removal after obstetric assessment.
Q14. How long is recovery after polyp removal?
Ans. Most women resume daily activities within 24–48 hours after hysteroscopic polypectomy.
Q15. Do polyps affect periods?
Ans. Yes, they often cause heavy periods, spotting, or irregular menstrual cycles.
