Ovarian Cyst Treatment in Goregaon West, Mumbai
Introduction
Are you experiencing pelvic pain, irregular periods, or bloating?
You could be dealing with an ovarian cyst—a common but often silent condition. At Vardaan Hospital, Goregaon West, expert gynecologist Dr. Dimple Doshi brings over 26 years of experience and the latest in 3D laparoscopic technology to provide accurate diagnosis and comprehensive treatment for all types of ovarian cysts, including hemorrhagic, paraovarian, borderline, and malignant cysts.
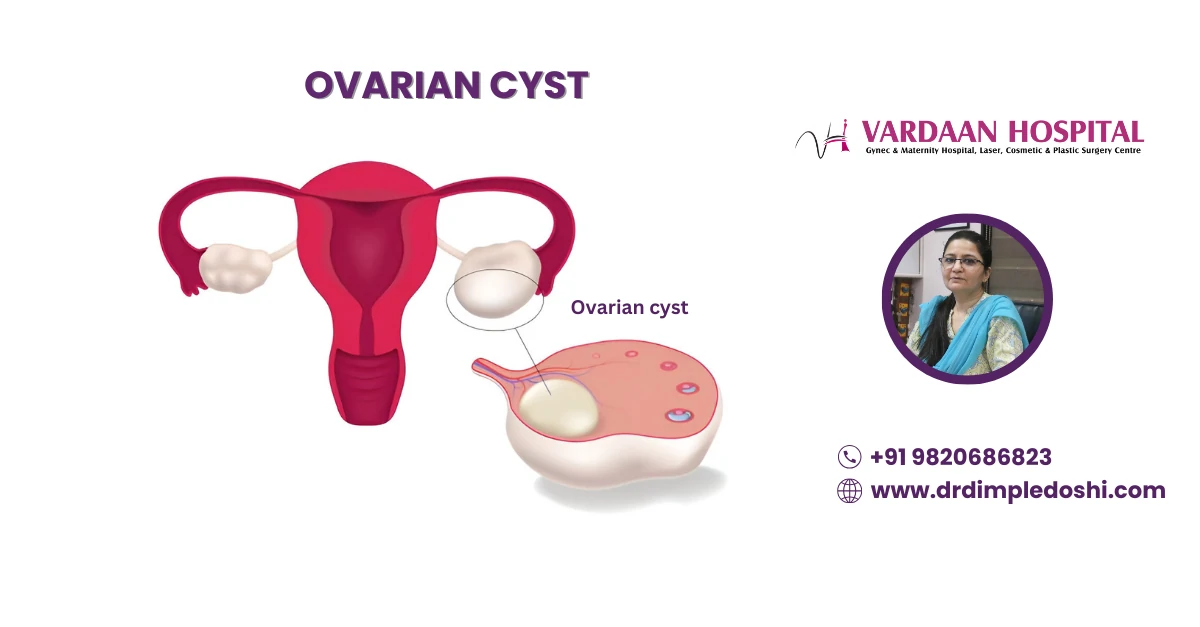
What Is an Ovarian Cyst?
An ovarian cyst is a fluid- or blood-filled sac that forms within or adjacent to the ovary. While many are harmless, others can cause pain, infertility, or even indicate early-stage cancer. Timely diagnosis and appropriate management are critical.
Synonyms of Ovarian Cyst:
- Ovary cyst
- Cyst on the ovary
- Ovarian growth
- Fluid-filled sac in the ovary
- Ovarian lump
- Cystic growth in ovary
- Pelvic cyst
What Are the Different Types of Ovarian Cysts?
Functional cysts (related to normal ovarian function), including:
Follicular cysts – when a follicle fails to release an egg during ovulation
Corpus luteum cysts – formed after ovulation when the corpus luteum seals and fills with fluid or blood
Theca lutein cysts – large, often bilateral cysts caused by excessive hCG stimulation (seen in molar pregnancy, multiple pregnancy, or fertility treatments)
- Hemorrhagic cysts (internal bleeding within cyst)
- Endometriomas (chocolate cysts in endometriosis)
- Dermoid cysts (teratomas containing hair, fat, or teeth)
- Cystadenomas (serous or mucinous cysts)
- Paraovarian cysts (arise adjacent to but separate from the ovary)
- Polycystic ovaries (PCOD/PCOS)
- Borderline ovarian tumors (low malignant potential)
- Malignant ovarian cysts (ovarian cancer)
Complex cysts—especially hemorrhagic, borderline, paraovarian, and malignant—require individualized care from an experienced gynecologist.
What Are the Common Symptoms of Ovarian Cysts and How Do They Affect You Emotionally?
Many ovarian cysts are silent, but others cause considerable distress. Women may suffer silently, fearing cancer or losing fertility.
Common Symptoms
- Lower abdominal or pelvic pain
- Menstrual irregularities
- Bloating and heaviness
- Pain during intercourse or bowel movements
- Fatigue, nausea, or spotting
- Sharp pain if cyst ruptures or twists
Hormonal imbalances, especially in PCOS
What Complications Can Arise from Untreated Ovarian Cysts?
If left untreated or mismanaged, ovarian cysts can cause serious health risks:
1. Ovarian Torsion
- Twisting of ovary due to a cyst
- Severe pain, vomiting; emergency surgery required
- Can cause loss of ovary if delayed
- Bulky polycystic ovaries and dermoid cysts are particularly prone to torsion
- Torsion may be intermittent—twisting and untwisting—causing recurrent pain
- In severe cases, necrosis of ovary may necessitate oophorectomy (removal of the ovary)
- Early detection allows laparoscopic detorsion with or without laparoscopic oophoropexy (surgical fixation of the ovary to prevent future torsion)
- Triggers: sudden forward bending, heavy lifting, abrupt posture changes, or intense physical activity
2. Cyst Rupture
- Sudden release of fluid or blood
- May lead to internal bleeding or peritonitis
- Common in hemorrhagic and cystadenomas
3. Infertility
- Endometriomas and PCOS-related cysts may impair ovulation
- Repeated surgeries or adhesions can damage ovarian reserve
- Paraovarian cysts may obstruct tubal function
4. Infection or Abscess Formation
- Rare, but possible in cysts post-rupture or with secondary infection
5. Malignant Transformation
- Some benign-looking cysts (dermoid, cystadenoma) may harbor malignancy
- Borderline tumors may recur or transform over time
6. Adhesions & Chronic Pelvic Pain
Due to rupture, torsion, or repeated inflammation/surgery
How Are Ovarian Cysts Diagnosed and Differentiated Between Harmless and Dangerous Ones?
At Vardaan Hospital, Dr. Doshi uses an evidence-based protocol:
- High-resolution transvaginal ultrasound with color Doppler
- MRI/CT for complex or suspicious masses
- CA-125, HE4, and other tumor markers
Diagnostic laparoscopy and frozen section, if needed
What Are the Available Treatment Options for Ovarian Cysts?
1. Medical Management – First Line for Selected Cysts
Ideal for:
- Functional cysts
- Small hemorrhagic cysts
- PCOS
- Mild endometriosis
Includes:
- Hormonal therapy (OCPs, progesterone)
- GnRH analogues for endometriosis
- Metformin in PCOS
- Pain relief with NSAIDs
- Iron and supplements for anemic patients
- Regular ultrasound monitoring
2. 3D Laparoscopic Surgery – Precision with Faster Recovery
Indications for Surgery:
- Ovarian torsion (especially dermoid or bulky polycystic ovaries)
- Suspicion of malignancy (solid-cystic mass, elevated CA-125)
- Persistent cyst not resolving after 2–3 cycles
- Large cysts (>5 cm postmenopausal, >8 cm reproductive age)
- Ruptured cyst causing bleeding
- Endometriomas (>4 cm or symptomatic)
- Rapidly growing or recurrent cysts
- Chronic pelvic pain or pressure symptoms
- Infertility due to cyst-related ovulatory or tubal dysfunction
- Painful intercourse
Indicated for:
- Persistent, painful, or large cysts
- Hemorrhagic, paraovarian, or borderline cysts
- Suspicious or malignant cysts
- Infertility-related cysts
Advantages of 3D Laparoscopic Surgery:
- Cutting Edge Karl Storz Rubina 4K 3D laparoscope, Excellent precision
- Minimally invasive, highly precise dissection
- Fertility-preserving cystectomy is don Best with 3d laparoscopic surgery
- Short hospital stay, faster healing, minimal scars
3. Advanced Surgery for Borderline or Malignant Cysts
- Cystectomy, oophorectomy, or full staging surgery
- Intraoperative frozen section biopsy
- Referral to oncologist if cancer is confirmed
Regular surveillance post-surgery for borderline tumors
Why Should You Choose Dr. Dimple Doshi for Ovarian Cyst Management?
- Over 26 years of gynecology and laparoscopic experience
- Expertise in complex cysts – hemorrhagic, paraovarian, borderline
- Advanced 3D laparoscopic surgery for precision care
- Fertility-sparing focus for reproductive-age women
- Personalized, evidence-based, and compassionate treatment
What Is the Medical Code for an Ovarian Cyst?
ICD-10 Codes for Ovarian Cysts:
- N83.0: Follicular cyst of the ovary
- N83.1: Corpus luteum cyst of the ovary
- N83.2: Other and unspecified ovarian cysts
- N83.201: Unspecified ovarian cyst on the other side
- N83.202: Unspecified ovarian cyst on the left side
- N83.209: Unspecified ovarian cyst on an unspecified side
CPT Codes for Ovarian Cysts (depending on the procedure):
- 58925: Ovarian cystectomy, unilateral or bilateral
- 58662: Laparoscopy, surgical; with fulguration or excision of lesions of the ovary, pelvic viscera, or peritoneal surface by any method (e.g., ovarian cystectomy)
- 58720: Salpingo-oophorectomy, complete or partial, unilateral or bilateral (if the ovarian cyst requires removal of the ovary and fallopian tube)
Reference: Codify by AAPC
Book a Consultation
Don’t let symptoms or fear delay your care. Whether it’s a simple functional cyst, a complex hemorrhagic lesion, a paraovarian mass, or a borderline tumor, expert help is one step away.



