Uterine Fibroid: Safe & Advanced Treatment for Better Health
Struggling with Heavy Periods or Bloating? You Might Have Fibroids
- Do your periods feel like a punishment—painful, long, heavy?
- Does your belly feel bloated, pressured, or tender?
- Do you constantly feel drained and fatigued?
- Are you always worried about getting your periods and unable to plan anything?
- Are you tired of changing pads every hour or avoiding travel, intimacy, and even pregnancy dreams?
You may be silently dealing with uterine fibroids.
These non-cancerous tumors often go undiagnosed until they start stealing your peace, energy, and fertility.
But you don’t have to live with this anymore.
At Vardaan Hospital, we offer both medical and surgical treatment for uterine fibroids.
Our advanced 3D laparoscopic fibroid surgery is minimally invasive, fertility-sparing, and recovery-friendly.
What Are Uterine Fibroids?
Uterine fibroids are non-cancerous growths of the uterus that commonly affect women aged 30–50, causing symptoms like heavy bleeding and pelvic pain.
- Also called leiomyomas or myomas
- Can be small and asymptomatic or large and painful
- Often shrink after menopause
What Are the Symptoms of Uterine Fibroids?
Symptoms vary by size and location, but many women experience heavy periods, pelvic pain, frequent urination, and fertility issues.
- Heavy menstrual bleeding (menorrhagia)
- Severe cramps and pelvic pressure
- Constipation or frequent urination
- Back pain, bloating, or painful intercourse
- Infertility, miscarriage, or anemia
What Causes Uterine Fibroids to Grow?
Fibroid growth is influenced by estrogen, progesterone, genetics, obesity, diet, inflammation, and environmental toxins.
- Hormones: Estrogen and progesterone stimulate growth
- Genetics: Certain mutations increase risk
- Diet & Lifestyle: High red meat, alcohol, low vitamin D
- Inflammation & Xenoestrogens: Promote fibroid development
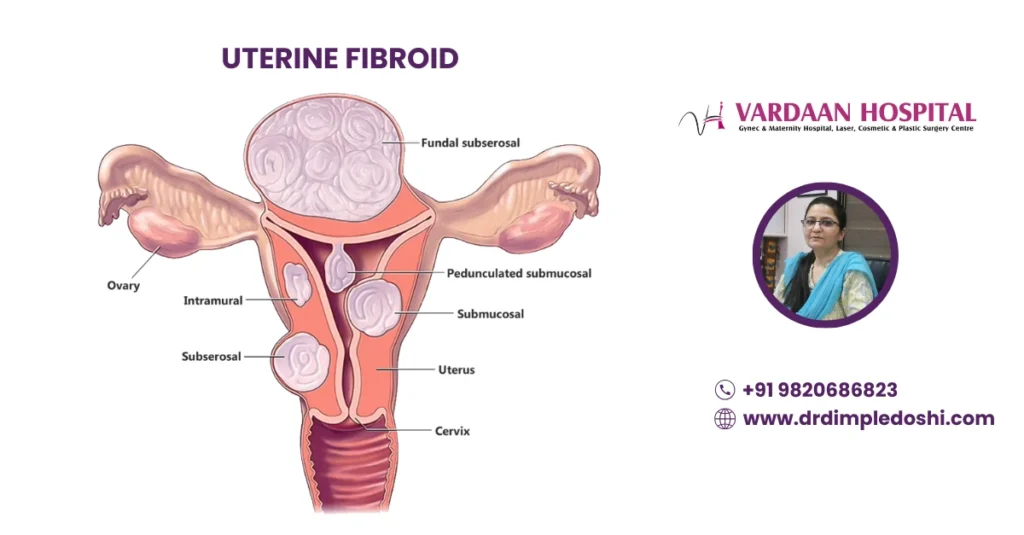
What Are the Different Types of Uterine Fibroids?
Fibroids are categorized by location—intramural, subserosal, submucosal, pedunculated, and cervical—each causing unique symptoms.
- Intramural: In uterine muscle wall (most common)
- Subserosal: On outer uterus (causes pressure)
- Submucosal: Into cavity (heavy bleeding, infertility)
- Pedunculated: On stalk (may twist and hurt)
- Cervical: In cervix (may cause blockage)
What Is the FIGO Classification of Fibroids?
The FIGO system classifies fibroids from Type 0 to 8 based on location, helping decide the best surgical approach.
| Type | Location |
|---|---|
| 0 | Pedunculated submucosal (in uterine cavity) |
| 1 | <50% intramural, mostly submucosal |
| 2 | ≥50% intramural, still submucosal |
| 3 | Contact with endometrium but 100% intramural |
| 4 | Completely intramural |
| 5 | Subserosal, ≥50% intramural |
| 6 | Subserosal, <50% intramural |
| 7 | Pedunculated subserosal |
| 8 | Other – cervical, parasitic |
How Are Fibroids Diagnosed?
Fibroids are diagnosed using ultrasound, MRI, and diagnostic procedures like hysteroscopy or laparoscopy based on symptoms and location.
- Clinical pelvic exam
- Transvaginal and abdominal ultrasound
- 3D transvaginal sonography (TVS)
- MRI for mapping large/multiple fibroids
- Hysteroscopy or diagnostic laparoscopy
What Are the Best Treatment Options for Fibroids?
Options range from hormone therapy and embolization to advanced 3D laparoscopic myomectomy or hysterectomy depending on fertility goals.
- Medical: Hormonal pills, GnRH analogs, tranexamic acid
- Non-surgical: Uterine artery embolization, MRI-guided HIFU
- Surgical: 3D laparoscopic myomectomy or hysterectomy
Why Choose 3D Laparoscopic Fibroid Surgery?
3D laparoscopic surgery offers better visualization, minimal scarring, faster healing, and lower recurrence compared to open surgery.
- High-definition depth and precision
- Less blood loss, faster recovery
- Tiny incisions and short hospital stay
- Preserves fertility in many cases
Who Is the Ideal Candidate for Fibroid Surgery?
Women with large, painful, bleeding fibroids or fertility challenges who want uterus-preserving options are good candidates for surgery.
- Heavy bleeding or pelvic pain
- Infertility or miscarriage
- Failed medication treatments
- Fibroid distortion of uterus or organs
What Happens Before and After Fibroid Surgery?
Surgery involves lab tests, imaging, 3D laparoscopic removal, 1–2 days of rest, and full recovery within 4–6 weeks.
- Before: Tests, anemia correction, fitness clearance
- During: General anesthesia, 3D laparoscopy
- After: Resume daily activities in 5–10 days
What Are the Risks of Fibroid Surgery?
Risks are rare in expert hands but may include bleeding, infection, organ injury, adhesions, or fibroid recurrence over time.
- Bleeding and infection
- Adhesion formation
- Injury to surrounding organs
What Results Can I Expect After Fibroid Surgery?
Most patients experience dramatic relief from symptoms, improved energy levels, better fertility, and a higher quality of life.
- Freedom from heavy bleeding and cramps
- Relief from fatigue and discomfort
- Fertility restoration after myomectomy
Why Choose Dr. Dimple Doshi for Fibroid Surgery?
Dr. Dimple Doshi is a pioneer in 3D laparoscopic fibroid surgery in Mumbai, with 25+ years of experience and 25,000+ surgeries performed.
Why Vardaan Hospital, Goregaon for Fibroid Treatment?
Vardaan Hospital offers cutting-edge 3D laparoscopy, all-women surgical staff, and a supportive, safe environment for women’s health.
- Located in Goregaon West, Mumbai
- Karl Storz 3D Rubina Suite
- Privacy, safety, and comfort prioritized
What Is the Cost of Fibroid Surgery in Mumbai?
Cost varies based on fibroid size, surgery type (laparoscopic or hysteroscopic), and hospital stay, but EMI and consultation options are available.
- Includes surgical fees and consumables
- Custom quotes available during consultation
Medical Codes for Uterine Fibroids
ICD-10 Codes for Uterine Fibroids
| ICD-10 Code | Description |
|---|---|
| D25.0 | Submucous leiomyoma of uterus |
| D25.1 | Intramural leiomyoma of uterus |
| D25.2 | Subserosal leiomyoma of uterus |
| D25.9 | Leiomyoma of uterus, unspecified |
CPT Codes for Uterine Fibroid Treatment
| CPT Code | Procedure |
|---|---|
| 58140 | Myomectomy, excision of fibroid tumors of uterus; abdominal approach |
| 58145 | Myomectomy (more extensive; multiple or deep intramural myomas) |
| 58146 | Myomectomy with complicated procedure or extensive adhesiolysis |
| 58545 | Laparoscopy, surgical; myomectomy (1–2 myomas, <5 cm) |
| 58546 | Laparoscopic myomectomy (>2 myomas or >5 cm) |
| 58558 | Hysteroscopy, surgical; with removal of leiomyomata |
| 58150 | Total abdominal hysterectomy (TAH) |
| 58570 | Laparoscopic total hysterectomy |
| 57425 | Uterine fibroid embolization (UFE), radiological supervision and interpretation |
(FAQ's) Frequently Asked Question of Uterine Fibroids
Q1. Is it safe to live with uterine fibroids?
Ans. Small, asymptomatic fibroids can be monitored without immediate treatment. However, larger fibroids or those causing symptoms like pain or bleeding may require medical attention.
Q2. What are the dangers of having fibroids?
Ans. Dangers include heavy bleeding, anemia, chronic pelvic pain, bladder/bowel pressure, fertility issues, and complications during pregnancy if untreated.
Q3. Can fibroids affect your period?
Ans. Yes, fibroids can cause heavy, prolonged, or irregular menstrual bleeding due to increased blood supply and distortion of the uterine lining.
Q4. Can fibroids be cancerous?
Ans. Most fibroids are benign. Less than 1% may develop into a rare cancer called leiomyosarcoma. Any rapid growth should be investigated further.
Q5. What happens if you don’t remove a uterine fibroid?
Ans. Fibroids may continue to grow and worsen symptoms like bleeding, pain, or infertility. Delayed treatment may also complicate future surgeries.
Q6. Can fibroids be removed without surgery?
Ans. Yes. Options include medications, uterine artery embolization, focused ultrasound, or hormone therapy. Surgery is advised if symptoms persist or fibroids are large.
Q7. What vitamins shrink fibroids?
Ans. Vitamin D, green tea extract (EGCG), and omega-3 fatty acids may help reduce fibroid size or inflammation. However, these are supportive and not substitutes for medical treatment.
Q8. Can stress cause fibroids?
Ans. Stress doesn’t directly cause fibroids, but it may influence hormonal imbalance which contributes to fibroid growth in some individuals.
Q9. Can a woman with fibroids get pregnant?
Ans. Many women with fibroids can conceive naturally. However, certain types, especially submucosal fibroids, can interfere with conception and may need treatment.
Q10. Can fibroids cause miscarriage?
Ans. Yes. Fibroids that distort the uterine cavity or interfere with placental implantation can increase the risk of miscarriage or preterm labor.
Q11. What happens to fibroids when periods stop?
Ans. After menopause, fibroids usually shrink due to decreased estrogen and progesterone levels. However, postmenopausal growth should be evaluated.
Q12. What deficiency causes uterine fibroids?
Ans. Low levels of vitamin D have been linked to fibroid development. However, fibroids are multifactorial, and no single deficiency is the root cause.
Q13. How do we prevent fibroids?
Ans. While not all fibroids are preventable, maintaining a healthy weight, managing estrogen levels, regular exercise, and possibly vitamin D supplementation may reduce risk.
Q14. Does vitamin D reduce fibroids?
Ans. Some studies suggest that vitamin D may slow fibroid growth or reduce size, especially in women with a deficiency. It’s considered a supportive therapy.
Q15. What is the fastest way to cure fibroids?
Ans. The quickest and most definitive treatment is surgery (laparoscopic myomectomy or hysterectomy). For non-surgical management, options depend on size, location, and symptoms.
Take charge of your health today.
Book your consultation with Dr. Dimple Doshi at
Vardaan Hospital, Goregaon West, Mumbai.

