Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS): Expert Care for Hormonal Balance
Irregular Periods, Weight Gain, or Acne? It Could Be PCOS
- Are you struggling with irregular periods, unexplained weight gain, or excessive hair growth?
- Do breakouts or thinning scalp hair leave you feeling frustrated and anxious?
These could be signs of Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS)—one of the most common hormonal disorders in women of reproductive age.
PCOS isn’t just about periods—it can affect your skin, mood, fertility, and long-term health. If ignored, it may lead to complications like diabetes, infertility, and heart disease. The constant cycle of symptoms can feel exhausting, impacting your confidence and quality of life.
The good news? PCOS is manageable with the right care. Through personalized lifestyle plans, hormonal balance, and medical treatment, you can regain control of your health and future fertility. At Vardaan Hospital, Dr. Dimple Doshi provides expert guidance and holistic management for PCOS, helping you feel healthy, confident, and in control again.
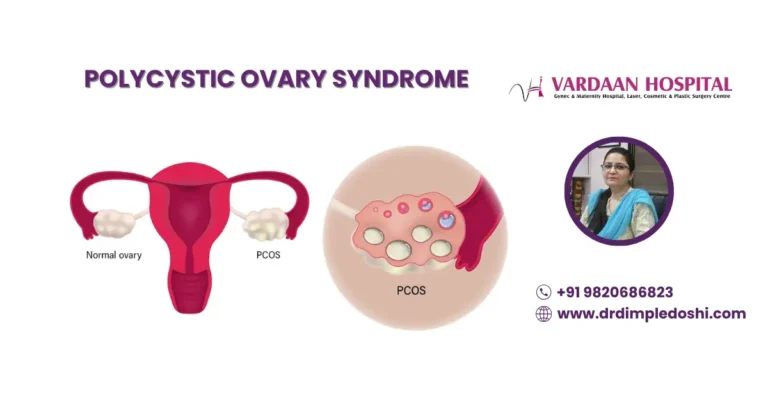
What Is PCOS (Polycystic Ovary Syndrome)?
PCOS is a hormonal disorder where the ovaries develop multiple small cysts, affecting ovulation and leading to irregular periods, acne, weight gain, and fertility issues.
According to FOGSI, 20-30% of women in India suffer from PCOS.
What Is the Incidence of (PCOS) Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome Worldwide and in India?
PCOS affects 1 in 10 women globally. In India, its prevalence ranges between 10% and 30% among women of reproductive age, with increasing cases due to lifestyle factors.
What Are the Common Symptoms of (PCOS) Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome?
Symptoms vary but often include:
- Excess facial or body hair (hirsutism)
- Scalp hair thinning (androgenic alopecia)
- Acne and oily skin
- Irregular or missed periods
- Obesity or difficulty losing weight
- Dark skin patches (Acanthosis Nigricans)
- Infertility or difficulty conceiving
How Are PCOS and PCOD Different?
While both conditions affect ovaries, PCOS is more severe and linked with higher health risks than PCOD. Here’s a quick comparison:
| Feature | PCOD | PCOS |
|---|---|---|
| Cause | Mild hormonal imbalance | Disruption of hormonal system |
| Impact | Mainly affects menstruation | Affects metabolism, BP, blood sugar |
| Severity | Milder, easier to treat | More severe and resistant |
| Pregnancy | Possible with medication | Difficult, may require IVF |
What Causes (PCOS) Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome?
PCOS has multiple triggers including:
- Insulin resistance leading to excess androgen
- Genetic predisposition (family history)
- Obesity and sedentary lifestyle
- Exposure to endocrine-disrupting chemicals
What Are the Risk Factors for (PCOS) Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome?
Key risk factors include:
- Family history of PCOS or diabetes
- High body mass index (BMI)
- Lack of physical activity
- Stress and poor sleep quality
How Is (PCOS) Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome Diagnosed?
Diagnosis is based on Rotterdam criteria and includes:
- Medical History: Irregular periods, symptoms
- Physical Exam: Hair growth, acne, weight
- Ultrasound: Detects ovarian cysts
- Blood Tests: Hormonal profile (LH, FSH, Testosterone), lipid and glucose tests
- Mental Health Screening: For depression and anxiety
What Are the Complications or Health Risks of (PCOS) Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome?
Untreated PCOS can lead to:
- Infertility
- Type 2 diabetes
- Heart disease and hypertension
- Endometrial cancer
- Depression and anxiety
What Are the Treatment Options for (PCOS) Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome?
PCOS treatment focuses on managing symptoms and improving fertility:
- Lifestyle Changes: Weight loss, healthy diet, exercise
- Medications:
- Hormonal pills for menstrual regulation
- Metformin for insulin resistance
- Spironolactone for hair and acne control
- Ovulation induction drugs for fertility
- Surgery: Laparoscopic ovarian drilling for resistant cases
What Should (PCOS) Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome Patients Eat and Avoid?
A PCOS-friendly diet improves insulin sensitivity and hormone balance:
- Eat: Whole grains, vegetables, lean proteins, healthy fats
- Avoid: Refined carbs, sugary drinks, processed foods, trans fats
What Are the Best Exercises for PCOS Management?
Exercise improves metabolism and hormonal health:
- Brisk walking or jogging
- Strength training
- Yoga and meditation for stress control
What Are the Long-Term Effects of (PCOS) Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome?
If untreated, PCOS can lead to:
- Diabetes and insulin resistance
- Heart disease and high cholesterol
- Endometrial cancer risk
- Depression, anxiety, and obesity-related issues
How to Manage (PCOS) Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome During Pregnancy?
PCOS increases pregnancy risks, so proper management is essential:
- Control weight before conception
- Monitor blood sugar and blood pressure
- Regular prenatal check-ups and medication adherence
What Is the Role of Stress Management in (PCOS) Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome?
Stress worsens hormonal imbalance in PCOS. Techniques include:
- Yoga and meditation
- Deep breathing exercises
- Counseling or therapy if needed
Who Is the Best Doctor for the Treatment of PCOS in Mumbai?
Dr. Dimple Doshi at Vardaan Hospital, Goregaon, specializes in PCOS treatment using advanced medical care and holistic wellness approaches.
Which Is the Best Hospital for PCOS Treatment in Goregaon, Mumbai?
Vardaan Hospital offers comprehensive PCOS care with modern diagnostics, expert doctors, and lifestyle support for long-term results.
What Are the Key Takeaways to Manage (PCOS) Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome Effectively?
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Follow a low-GI, high-fiber diet
- Exercise regularly and reduce stress
- Monitor health and follow up with your doctor
FAQs – (PCOS) Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome
Q1. What is PCOS and why does it happen?
Ans. PCOS (Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome) is a hormonal disorder where ovaries produce excess androgens, leading to irregular periods, cysts, and fertility issues. Causes include genetics, insulin resistance, and hormonal imbalance.
Q2. What are the most common symptoms of PCOS?
Ans. Symptoms include irregular periods, excessive hair growth, weight gain, acne, thinning scalp hair, and difficulty conceiving.
Q3. What causes PCOS in women?
Ans. The exact cause is unknown, but factors like insulin resistance, excess androgens, and family history play a major role.
Q4. Can PCOS be cured permanently?
Ans. There is no permanent cure for PCOS, but symptoms can be effectively managed with lifestyle changes, medications, and hormone therapy.
Q5. What are the treatment options for PCOS?
Ans. Treatments include lifestyle changes (diet & exercise), oral contraceptives for cycle regulation, anti-androgen medications, fertility treatments like ovulation induction, and insulin-sensitizing drugs.
Q6. Can PCOS affect fertility?
Ans. Yes, PCOS can cause ovulation problems leading to infertility. However, proper treatment can help restore ovulation and improve fertility.
Q7. How do doctors diagnose PCOS?
Ans. Diagnosis is based on the Rotterdam criteria: irregular periods, signs of excess androgens, and ultrasound showing polycystic ovaries.
Q8. Does PCOS get worse with age?
Ans. PCOS symptoms can change over time, but with proper management, complications like diabetes and heart disease can be prevented.
Q9. Can women with PCOS have a normal pregnancy?
Ans. Yes, many women with PCOS conceive naturally or with fertility treatment. Maintaining a healthy weight and following medical advice improves pregnancy outcomes.
Q10. How can PCOS be managed naturally?
Ans. Natural management includes weight control, balanced diet (low-carb, high-fiber), regular exercise, stress management, and avoiding processed foods.
Q11. What diet is best for PCOS?
Ans. A diet rich in whole grains, lean proteins, vegetables, and healthy fats with reduced sugar and processed foods helps manage PCOS symptoms.
Q12. Can PCOS cause hair loss and acne?
Ans. Yes, high androgen levels in PCOS can lead to male-pattern hair thinning and acne.
Q13. Is PCOS linked to other health problems?
Ans. Yes, PCOS increases the risk of diabetes, high cholesterol, heart disease, obesity, and depression.
Q14. How often should you visit a doctor for PCOS?
Ans. Regular checkups every 6 to 12 months are recommended to monitor symptoms, weight, blood sugar, and hormone levels.
Q15. Can PCOS be prevented?
Ans. PCOS cannot always be prevented, but healthy lifestyle habits like weight control, regular exercise, and balanced diet can lower the risk and manage symptoms effectively.
Medical Code for Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS)
ICD-10 Codes for Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
| ICD-10 Code | Description |
|---|---|
| E28.2 | Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) |
| E28.8 | Other specified ovarian dysfunction |
| E28.9 | Ovarian dysfunction, unspecified |
| N97.0 | Female infertility associated with anovulation (often linked to PCOS) |
CPT Codes for PCOS Treatment
| CPT Code | Procedure |
|---|---|
| 99213 | Office or other outpatient visit for evaluation and management (low complexity) |
| 99214 | Office or other outpatient visit for evaluation and management (moderate complexity) |
| 83036 | Hemoglobin A1C test (for insulin resistance monitoring) |
| 80061 | Lipid panel (monitoring cholesterol in PCOS patients) |
| 84443 | Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) test (rule out thyroid disorders) |
| 76830 | Transvaginal ultrasound for ovarian cyst detection |
| 76856 | Pelvic ultrasound, complete |
| 96372 | Therapeutic injection (for medications like insulin sensitizers or hormone therapy) |
Take charge of your health today.
Book your consultation with Dr. Dimple Doshi at
Vardaan Hospital, Goregaon West, Mumbai.


 WhatsApp
WhatsApp +91-9820686823
+91-9820686823 Book Appointment
Book Appointment