Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID): Get Relief with Expert Care
Lower Abdominal Pain, Fever, or Unusual Discharge? It Could Be PID
Are you experiencing persistent lower abdominal pain, fever, or foul-smelling vaginal discharge? These symptoms could signal Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)—a serious infection of the reproductive organs, including the uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries.
Ignoring PID can lead to severe consequences, such as chronic pelvic pain, ectopic pregnancy, or even infertility. Many women delay treatment due to embarrassment or lack of awareness, putting their future health and fertility at risk.
The good news: PID is treatable with early diagnosis and proper care. At Vardaan Hospital, Dr. Dimple Doshi offers expert evaluation and evidence-based treatment to eliminate infection and prevent complications. Your health—and your future—are too important to wait. Get treated before it’s too late.
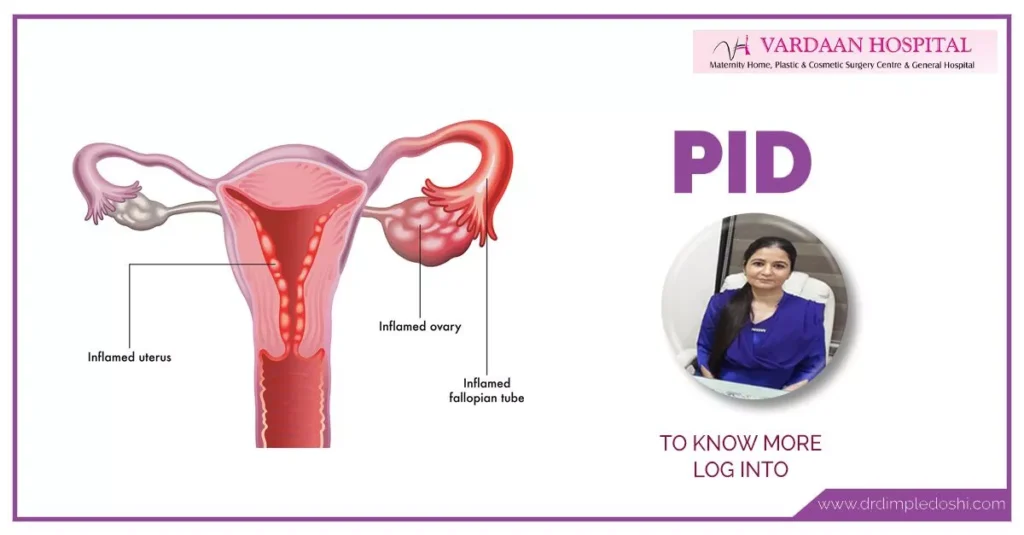
What Is Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)?
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID) is an infection of the female reproductive organs, usually caused by untreated sexually transmitted infections like chlamydia or gonorrhea.
- Affects the uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries
- Can lead to infertility or chronic pelvic pain if untreated
- Early diagnosis and treatment are essential
Synonyms: PID infection, pelvic infection, female reproductive tract infection, upper genital tract infection
What Causes Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)?
PID usually occurs when bacteria spread from the vagina to the uterus, fallopian tubes, or ovaries. Common causes include:
- Sexually transmitted infections: Chlamydia, Gonorrhea
- Pelvic tuberculosis (rare)
- Insertion of copper-T or hormone-based IUD without proper screening
- Post-abortion or childbirth infections
What Are the Risk Factors for Pelvic Inflammatory Disease?
Certain behaviors and conditions increase the risk of PID:
- Multiple sexual partners or unprotected sex
- History of STIs
- Douching or poor genital hygiene
- Insertion of IUD without proper screening
What Are the Symptoms of Pelvic Inflammatory Disease?
Symptoms may be mild or severe, making early detection crucial:
- Severe lower abdominal or pelvic pain
- Abnormal vaginal discharge (green/yellow, foul-smelling)
- Pain during sex (dyspareunia)
- Burning sensation while urinating
- Fever, chills, nausea, or vomiting
- Irregular menstrual bleeding
How Does Pelvic Inflammatory Disease Progress in the Body?
The infection starts in the lower reproductive tract and can spread to:
- Uterus (endometritis)
- Fallopian tubes (salpingitis)
- Ovaries (oophoritis)
- May lead to tubo-ovarian abscess if untreated
How Is Pelvic Inflammatory Disease Diagnosed?
PID diagnosis is based on clinical symptoms and confirmed through tests:
- Medical and sexual history evaluation
- Pelvic examination for tenderness
- Blood tests and urine analysis
- Ultrasound imaging of reproductive organs
- Endometrial biopsy (in select cases)
- Laparoscopy for definitive diagnosis
What Are the Serious Complications of Pelvic Inflammatory Disease?
Delayed or untreated PID can lead to severe complications:
- Infertility: Blocked or damaged fallopian tubes
- Ectopic pregnancy: Risk increases due to tubal scarring
- Chronic pelvic pain: Lasting months or years
- Tubo-ovarian abscess: Pus-filled infection requiring surgery
What Are the Treatment Options for Pelvic Inflammatory Disease?
Early treatment is crucial to prevent permanent damage:
- Oral antibiotics: Complete the full course as prescribed
- IV antibiotics: For severe infections or during pregnancy
- Hospitalization: If symptoms are severe or abscess forms
- Surgery: Rare, needed for abscess drainage
Important: Medicines cannot reverse existing damage; early treatment is key.
What Is the Role of Partner Treatment in Managing PID?
Sexual partners must be treated to prevent reinfection:
- Partners should be screened for STIs
- Avoid sexual contact until both partners are cleared
What Are the Prevention Options for Pelvic Inflammatory Disease?
Prevention focuses on reducing STI risk and early treatment:
- Practice safe sex (use condoms consistently)
- Limit number of sexual partners
- Avoid douching
- Regular gynecological check-ups
- Get prompt treatment for any vaginal infections
When Should You See a Doctor for PID Symptoms?
Seek medical help immediately if you experience:
- Severe pelvic or abdominal pain
- High fever and chills
- Nausea and vomiting
- Unusual or foul-smelling discharge
Medical Codes for Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)
ICD-10 Codes for Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)
| ICD-10 Code | Description |
|---|---|
| N73.0 | Acute parametritis and pelvic cellulitis |
| N73.1 | Chronic parametritis and pelvic cellulitis |
| N73.2 | Unspecified parametritis and pelvic cellulitis |
| N73.3 | Acute pelvic peritonitis in female |
| N73.4 | Chronic pelvic peritonitis in female |
| N73.5 | Unspecified pelvic peritonitis in female |
| N73.6 | Female pelvic peritoneal adhesions |
| N73.9 | Female pelvic inflammatory disease, unspecified |
CPT Codes for Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)
| CPT Code | Procedure |
|---|---|
| 99213 | Office or other outpatient visit for evaluation and management (low complexity) |
| 99214 | Office or other outpatient visit for evaluation and management (moderate complexity) |
| 87210 | Wet mount for infectious agents (vaginal/cervical) |
| 87070 | Bacterial culture (general, including PID pathogens) |
| 87591 | Infectious agent detection by nucleic acid (Chlamydia trachomatis) |
| 87592 | Infectious agent detection by nucleic acid (Neisseria gonorrhoeae) |
| 96372 | Therapeutic injection (for antibiotic administration) |
FAQs – Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)
Q1. What is Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)?
Ans. PID is an infection of the female reproductive organs, including the uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries, usually caused by sexually transmitted bacteria.
Q2. What causes Pelvic Inflammatory Disease?
Ans. The most common cause of PID is untreated sexually transmitted infections like chlamydia or gonorrhea. Poor hygiene, multiple partners, and unprotected sex can also increase risk.
Q3. What are the common symptoms of PID?
Ans. Symptoms include pelvic pain, abnormal vaginal discharge, fever, pain during intercourse, irregular periods, and painful urination. Some women may have mild or no symptoms.
Q4. Can PID be cured permanently?
Ans. Yes, with timely treatment using antibiotics, PID can be cured. However, any damage to reproductive organs caused by PID may not be reversible.
Q5. Can Pelvic Inflammatory Disease cause infertility?
Ans. Yes, untreated PID can lead to scarring and blockages in the fallopian tubes, causing infertility or increasing the risk of ectopic pregnancy.
Q6. How is PID diagnosed?
Ans. Diagnosis is based on symptoms, pelvic examination, vaginal swab tests, ultrasound, or in severe cases, laparoscopy for direct visualization.
Q7. What is the best treatment for PID?
Ans. PID is treated with a combination of antibiotics. Severe cases may require hospitalization or surgery if abscesses form.
Q8. Can you get pregnant after having PID?
Ans. Yes, if treated early, many women can conceive. However, multiple episodes or delayed treatment can reduce fertility chances.
Q9. Can PID be transmitted to a partner?
Ans. While PID itself is not transmitted, the bacteria that cause PID (such as chlamydia and gonorrhea) can be sexually transmitted, so partners should also be treated.
Q10. How do I reduce pelvic inflammation naturally?
Ans. While antibiotics are essential, natural measures like a healthy diet, hydration, rest, and avoiding unprotected sex during treatment can aid recovery.
Q11. How does PID pain feel?
Ans. PID pain is often a dull or sharp ache in the lower abdomen or pelvis, sometimes radiating to the lower back. Pain may worsen during sex or urination.
Q12. Can stress cause pelvic pain?
Ans. Stress itself doesn’t cause PID but can worsen perceived pain. Pelvic pain should always be evaluated by a doctor for possible infections or complications.
Q13. What happens if PID is left untreated?
Ans. Untreated PID can lead to chronic pelvic pain, infertility, ectopic pregnancy, and severe infections requiring emergency treatment.
Q14. How can PID be prevented?
Ans. Prevention includes practicing safe sex (using condoms), limiting the number of sexual partners, and regular screening for STIs.
Q15. When should I see a doctor for PID?
Ans. If you experience persistent pelvic pain, unusual discharge, fever, or pain during sex, seek medical attention immediately to prevent complications.
Take charge of your health today.
Book your consultation with Dr. Dimple Doshi at
Vardaan Hospital, Goregaon West, Mumbai.


 WhatsApp
WhatsApp +91-9820686823
+91-9820686823 Book Appointment
Book Appointment