Ovarian Cyst: Get Expert Treatment for Lasting Relief
Pelvic Pain, Irregular Periods, or Bloating? It Could Be an Ovarian Cyst
Are you struggling with sudden pelvic pain, irregular menstrual cycles, or persistent bloating? These symptoms might indicate an ovarian cyst—a condition many women experience without even realizing it.
While some ovarian cysts are harmless and go away on their own, others can cause severe pain, rupture, or even impact fertility. Ignoring these symptoms can lead to emergency situations or missed chances for early treatment of complex cysts, including borderline or malignant ones.
The good news? Most ovarian cysts are treatable—and often with minimally invasive methods.
At Vardaan Hospital, Goregaon West, Dr. Dimple Doshi, with 26+ years of expertise and advanced 3D laparoscopic technology, offers accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment for all types of ovarian cysts, including hemorrhagic, paraovarian, borderline, and malignant cysts. Our goal: safe, precise, and fertility-friendly care for every woman.
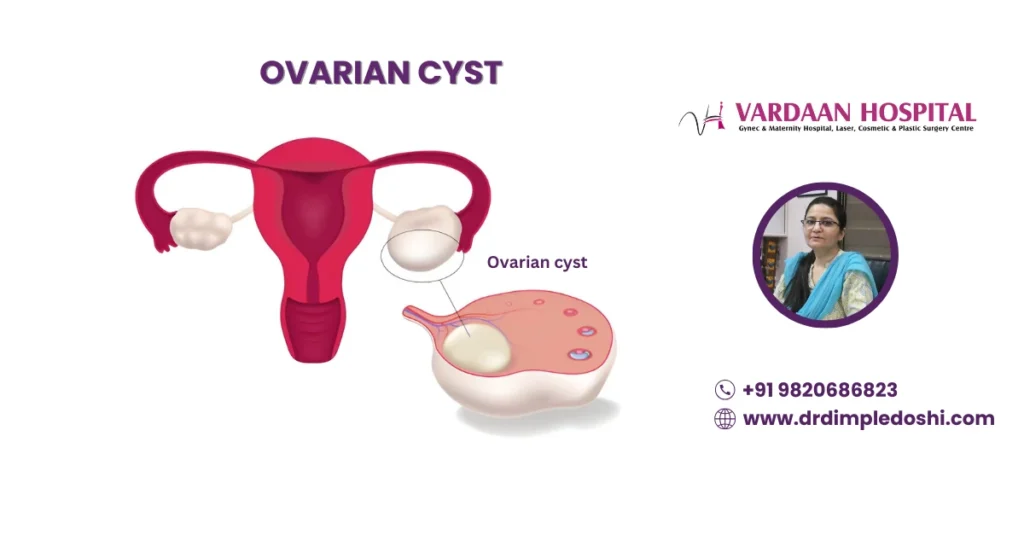
What Is an Ovarian Cyst?
An ovarian cyst is a fluid- or blood-filled sac that develops on or inside an ovary. Most are harmless, but some can lead to pain, fertility issues, or rarely cancer.
- Often detected during routine pelvic exams or ultrasound
- Common in women of reproductive age
- Early diagnosis helps prevent complications
Synonyms: Ovary cyst, ovarian growth, cyst on ovary, pelvic cyst, cystic growth in ovary
What Is the Incidence of Ovarian Cysts in Women?
Ovarian cysts are very common in women of reproductive age. Around 8% to 18% of women will develop a cyst in their lifetime, with most being harmless and functional.
- Functional cysts account for the majority of cases
- Common during reproductive years due to hormonal cycles
- Most cysts resolve naturally without treatment
What Are the Different Types of Ovarian Cysts?
Ovarian cysts vary based on their origin and severity. Most are benign, but some require treatment or surgical removal for safety.
- Functional Cysts: Follicular cysts, corpus luteum cysts, theca lutein cysts
- Hemorrhagic Cysts: Contain internal bleeding within the cyst
- Endometriomas: Known as “chocolate cysts” caused by endometriosis
- Dermoid Cysts: Contain tissue such as hair, fat, or teeth
- Cystadenomas: Fluid-filled, can be serous or mucinous
- Paraovarian Cysts: Develop adjacent to but separate from the ovary
- Polycystic Ovaries (PCOS): Multiple small cysts on the ovary surface
- Borderline Tumors: Low malignant potential
- Malignant Cysts: Indicate ovarian cancer
What Are the Causes and Risk Factors for Ovarian Cysts?
Ovarian cysts often develop due to hormonal fluctuations, ovulatory problems, or conditions like PCOS and endometriosis. Some risk factors increase susceptibility.
- Common Causes:
- Hormonal imbalances and ovulatory dysfunction
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) or endometriosis
- Pregnancy-related cyst formation
- Previous ovarian or pelvic surgery
- Risk Factors:
- Family history of ovarian cysts or PCOS
- Obesity and poor lifestyle habits
- Smoking and excessive alcohol intake
- Use of fertility treatments or hormone therapies
What Are the Common Symptoms of Ovarian Cysts and How Do They Affect You Emotionally?
Many cysts are silent, but others cause physical pain and emotional stress:
- Pelvic or lower abdominal pain
- Irregular menstrual cycles
- Bloating and heaviness
- Painful intercourse
- Nausea or fatigue
- Sharp pain with cyst rupture or torsion
Emotional Impact: Anxiety about infertility and cancer risk can cause significant stress.
What Complications Can Arise from Untreated Ovarian Cysts?
If left untreated, ovarian cysts can cause serious issues such as pain, infertility, or, in rare cases, cancer. Timely diagnosis helps prevent these risks.
- Ovarian torsion: Twisting of the ovary causing severe pain and possible loss of the ovary
- Cyst rupture: Leads to internal bleeding and infection
- Infertility: Common with endometriomas or severe PCOS
- Malignant transformation: Rare, but some cysts may turn cancerous
- Adhesions & chronic pelvic pain: Due to rupture or repeated surgeries
How Are Ovarian Cysts Diagnosed and Differentiated Between Harmless and Dangerous Ones?
Ovarian cysts are diagnosed using imaging and blood tests to assess size, structure, and cancer risk. Most are benign, but detailed evaluation is essential.
- Transvaginal ultrasound with color Doppler: First-line imaging for size, type, and blood flow
- MRI or CT scan: For complex or suspicious cysts
- Tumor markers: CA-125, HE4 help assess ovarian cancer risk
- Diagnostic laparoscopy: For direct visualization when needed
What Are the Treatment Options for Ovarian Cysts?
Treatment depends on size, type, and symptoms:
- Medical Management: Hormonal therapy, GnRH analogues, Metformin (PCOS), NSAIDs for pain
- 3D Laparoscopic Surgery: For persistent, large, or suspicious cysts; fertility-preserving techniques available
- Oncological Surgery: For borderline or malignant cysts with frozen section biopsy
What Is the Recovery Like After Ovarian Cyst Surgery?
Recovery is usually quick after laparoscopy:
- Hospital stay: 1 day
- Return to work: 1-2 weeks
- Minimal scarring and faster healing
How Can Ovarian Cysts Affect Fertility and Pregnancy?
Ovarian cysts, especially large cysts or endometriomas, can reduce ovarian reserve, interfere with ovulation, and impact natural conception or IVF success.
- Endometriomas may damage healthy ovarian tissue
- Large cysts can hinder egg release or block fallopian tubes
- PCOS-related cysts often cause irregular ovulation
- Surgery aims to preserve eggs and improve fertility outcomes
When Should You See a Doctor for Ovarian Cyst Symptoms?
Seek immediate care if you experience:
- Sudden severe pelvic pain
- Fainting or dizziness
- Rapid bloating or persistent nausea
Can Ovarian Cysts Be Prevented?
You cannot prevent all cysts, but you can reduce risk with:
- Regular gynecological check-ups
- Managing PCOS and hormonal disorders
- Avoiding unnecessary hormone medications
Why Should You Choose Dr. Dimple Doshi for Ovarian Cyst Management?
Dr. Dimple Doshi offers expert care for ovarian cysts with advanced laparoscopic techniques and a strong focus on fertility preservation.
- 26+ years of experience in gynecology and minimally invasive surgery
- Specialized in 3D laparoscopic procedures for precision and safety
- Fertility-preserving approach for women of reproductive age
- Comprehensive pre- and post-operative care for better outcomes
Which Is the Best Hospital for Ovarian Cyst Surgery in Goregaon, Mumbai?
Vardaan Hospital is a top choice for ovarian cyst surgery in Goregaon, Mumbai, offering advanced laparoscopic care and experienced gynecological specialists.
- State-of-the-art facilities for minimally invasive gynecologic surgery
- Specialized in advanced 3D laparoscopic and fertility-preserving techniques
- Comprehensive patient care with personalized treatment plans
- Trusted for safety, high success rates, and compassionate support
What Is the Medical Code for an Ovarian Cyst?
ICD-10 Codes for Ovarian Cyst
| ICD-10 Code | Description |
|---|---|
| N83.0 | Follicular cyst of ovary |
| N83.1 | Corpus luteum cyst |
| N83.2 | Other and unspecified ovarian cyst |
| N83.20 | Unspecified ovarian cyst, unspecified side |
| N83.201 | Unspecified ovarian cyst, right side |
| N83.202 | Unspecified ovarian cyst, left side |
| N83.209 | Unspecified ovarian cyst, bilateral |
CPT Codes for Ovarian Cyst Treatment
| CPT Code | Procedure |
|---|---|
| 99213 | Office or other outpatient visit for evaluation and management (low complexity) |
| 99214 | Office or other outpatient visit for evaluation and management (moderate complexity) |
| 76830 | Transvaginal ultrasound for ovarian cyst detection |
| 76856 | Pelvic ultrasound, complete |
| 58661 | Laparoscopy, surgical; with removal of adnexal structures (partial or total oophorectomy) |
| 58662 | Laparoscopy, surgical; with removal of adnexal structures (including ovarian cystectomy) |
| 58925 | Ovarian cystectomy, open approach |
| 96372 | Therapeutic injection (for hormonal therapy) |
FAQs – Ovarian Cysts Diagnosis and Treatment
Q1. What are the early warning signs of an ovarian cyst?
Ans. Common early signs include pelvic pain, bloating, feeling full quickly, and changes in menstrual cycles. Severe pain may indicate a ruptured or twisted cyst, which requires urgent care.
Q2. How serious is an ovarian cyst?
Ans. Most ovarian cysts are harmless and resolve on their own. However, large cysts or those causing severe pain, bleeding, or rupture may need immediate medical attention.
Q3. Can an ovarian cyst affect fertility?
Ans. Functional cysts usually do not affect fertility, but conditions like PCOS or endometriomas can impact ovulation and conception.
Q4. Can you get pregnant with an ovarian cyst?
Ans. Yes, in most cases, pregnancy is possible with functional cysts. However, large or complex cysts may require treatment before conception.
Q5. What is the best treatment for an ovarian cyst?
Ans. Treatment depends on the type and size of the cyst. Options include watchful waiting, hormonal therapy, or surgical removal if the cyst is large or symptomatic.
Q6. Do all ovarian cysts require surgery?
Ans. No. Small, functional cysts often resolve naturally. Surgery is recommended for persistent, large, or suspicious cysts.
Q7. Can an ovarian cyst burst?
Ans. Yes, cyst rupture can cause sudden severe pain, nausea, and internal bleeding. This is a medical emergency requiring immediate care.
Q8. What foods help shrink ovarian cysts naturally?
Ans. A diet rich in fiber, lean proteins, anti-inflammatory foods, and reduced refined sugars may support hormonal balance and cyst management.
Q9. How do you know if an ovarian cyst is harmful?
Ans. Cysts causing severe pain, rapid growth, irregular periods, or those appearing complex on ultrasound may be harmful and need further evaluation.
Q10. Which size ovarian cyst is considered dangerous?
Ans. Cysts larger than 5–6 cm or those growing rapidly often require monitoring or surgical removal to avoid complications.
Q11. Can an ovarian cyst delay your period?
Ans. Yes, hormonal imbalance due to ovarian cysts can delay or disrupt menstrual cycles.
Q12. Can an ovarian cyst go away on its own?
Ans. Functional cysts often disappear within 1–3 menstrual cycles without treatment.
Q13. What exercise is safe with an ovarian cyst?
Ans. Low-impact exercises like walking, yoga, and swimming are usually safe. Avoid heavy lifting if the cyst is large or painful.
Q14. What are the complications of untreated ovarian cysts?
Ans. Complications can include rupture, infection, internal bleeding, and ovarian torsion, which can damage the ovary.
Q15. When should you see a doctor for an ovarian cyst?
Ans. Seek immediate care if you experience sudden severe pelvic pain, dizziness, fainting, fever, or vomiting along with cyst symptoms.
Take charge of your health today.
Book your consultation with Dr. Dimple Doshi at
Vardaan Hospital, Goregaon West, Mumbai.


 WhatsApp
WhatsApp +91-9820686823
+91-9820686823 Book Appointment
Book Appointment