Endometriosis Treatment in Mumbai – Relieve Pain & Restore Fertility
What If Your Period Pain Isn’t “Normal”?
- Do your periods leave you curled up in bed, missing work, or feeling drained every month?
- Do you also experience severe pain while passing stools or even notice blood in your urine during periods?
These aren’t just “bad cramps”—they could be signs of endometriosis, a chronic condition affecting 1 in 10 women of reproductive age.
Unfortunately, many women endure this pain silently for years, being told it’s “just part of being a woman.” The truth? It’s not normal. Left untreated, endometriosis can cause chronic pelvic pain, digestive or urinary issues, and even infertility—deeply impacting physical, emotional, and social well-being.
The Good News: endometriosis is treatable.
At Vardaan Hospital, Goregaon West, Dr. Dimple Doshi, a senior laparoscopic surgeon with 27+ years of experience, offers advanced, fertility-preserving solutions—including 3D laparoscopic surgery using Karl Storz Rubina technology. Our approach focuses on precision, faster recovery, and restoring your quality of life.
What Is Endometriosis?
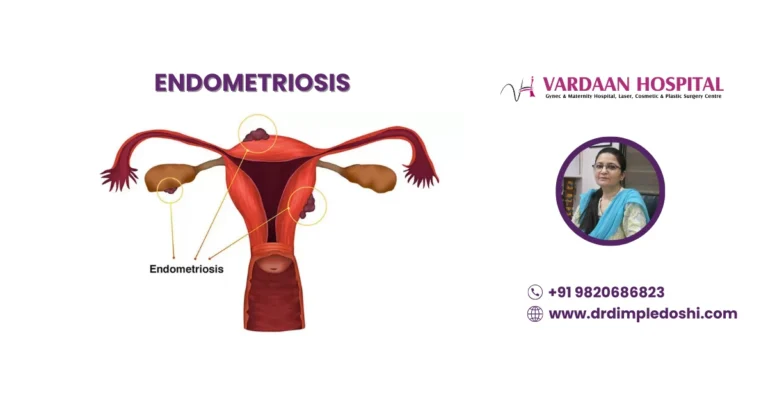
Endometriosis is a painful condition where tissue similar to the uterine lining (endometrium) grows outside the uterus, commonly on the ovaries, fallopian tubes, bladder, or pelvic wall.
- This tissue responds to hormonal changes and bleeds during periods
- Blood has no outlet, leading to inflammation and pelvic pain
- Causes scarring, adhesions, and sometimes ovarian cysts called “chocolate cysts” (endometriomas)
What Are the Symptoms of Endometriosis?
Endometriosis symptoms often go undetected on scans but can significantly disrupt daily life and fertility. Common signs include:
- Severe menstrual pain that worsens over time (dysmenorrhea)
- Painful intercourse (dyspareunia)
- Chronic pelvic pain or persistent lower back ache
- Painful urination or bowel movements during periods
- Fatigue, bloating, or nausea linked to your menstrual cycle
- Infertility or trouble conceiving despite regular attempts
Reminder: Pain that disrupts your quality of life is NOT normal. Seek medical evaluation early.
What Causes Endometriosis?
The exact cause of endometriosis isn’t fully understood, but several factors are believed to contribute to the condition.
- Retrograde menstruation: Menstrual blood flows backward into the pelvic cavity
- Hormonal imbalances: Estrogen dominance can stimulate abnormal tissue growth
- Genetics: Family history increases susceptibility
- Immune system issues: Failure to clear misplaced endometrial-like cells
- Embryonic cell transformation: Early developmental changes leading to abnormal tissue growth
How Is Endometriosis Classified?
Endometriosis severity is mapped using two widely accepted systems: ASRM staging and the latest Enzian classification (2021) for accurate diagnosis and surgical planning.
ASRM Staging (American Society for Reproductive Medicine)
This system stages endometriosis from minimal to severe based on lesion depth, presence of cysts, and adhesions.
| Stage | Severity | Description |
|---|---|---|
| I | Minimal | Few superficial lesions, no cysts |
| II | Mild | Slightly deeper implants, minimal adhesions |
| III | Moderate | Presence of ovarian endometriomas, some scarring |
| IV | Severe | Large chocolate cysts, dense pelvic adhesions |
Enzian Classification – 2021 (Advanced System)
This modern system maps deep infiltrating endometriosis (DIE), involving organs like bowel, bladder, ureters, and nerves for precise surgical planning.
| Code | Region | Common Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| A | Vagina / rectovaginal septum | Painful intercourse |
| B | Uterosacral ligaments | Back pain or pelvic pain |
| C | Rectum / sigmoid colon | Painful bowel movements |
| F | Bladder, ureter, diaphragm | Urinary or chest pain |
| O | Ovaries (endometriomas) | Infertility, cyst pain |
| T | Fallopian tubes | Blocked tubes |
| P | Peritoneum | Chronic pelvic pain |
At Vardaan Hospital, Dr. Dimple Doshi uses these classifications to plan precise 3D laparoscopic excision, ensuring complete removal of visible and hidden disease.
What Are the Different Types of Endometriosis?
Endometriosis can affect different pelvic structures and is classified into three main types based on location and severity.
- Peritoneal Endometriosis: The most common form where small lesions grow on the peritoneum (lining of the pelvis).
- Ovarian Endometrioma (Chocolate Cyst): Cysts filled with old blood that form on or inside the ovaries, often causing severe pain and infertility.
- Deep Infiltrating Endometriosis (DIE): Advanced form where endometrial-like tissue penetrates deeper into pelvic organs such as bowel, bladder, and uterosacral ligaments.
How Is Endometriosis Diagnosed?
Endometriosis diagnosis combines clinical evaluation with advanced imaging and minimally invasive techniques for confirmation.
- Detailed history & pelvic exam: Assess pain patterns and tenderness
- Pelvic ultrasound: Detects ovarian cysts (endometriomas) or adhesions
- MRI scan: Identifies deep infiltrating endometriosis and pelvic structures
- Diagnostic laparoscopy: Gold standard to visualize and treat lesions simultaneously
Note: Research is ongoing for blood tests and biomarkers to aid early detection of endometriosis.
What Are the Complications of Endometriosis?
Endometriosis tissue behaves like the uterine lining—it thickens and bleeds each cycle but cannot exit the body. This causes:
- Inflammation and internal bleeding
- Scar tissue and adhesions
- Ovarian cyst formation
- Progressive organ damage
These complications often develop silently over time and may only become noticeable when symptoms worsen or fertility issues arise.
12 Common Complications of Endometriosis
- Chronic Pelvic Pain: Persistent pain in the lower abdomen, back, or during sex, urination, or bowel movement, affecting sleep and daily life.
- Difficulty Conceiving: A leading cause of female infertility, endometriosis can block fallopian tubes, alter pelvic anatomy, and affect egg quality.
- Ovarian Cysts (Endometriomas or Chocolate Cysts): Fluid-filled cysts that may damage ovaries or reduce egg reserve. Larger cysts may require surgery.
- Internal Scarring and Adhesions: Abnormal tissue sticking organs together, causing:
- Severe pelvic pain
- Bowel and urinary difficulties
- Complex future surgeries (e.g., “frozen pelvis”)
- Bowel and Bladder Problems: Endometriosis on these organs can cause:
- Pain during urination or bowel movement
- Blood in urine or stool during periods
- Bloating, constipation, or urinary urgency
- Kidney Damage (Silent but Serious): Blocked ureters can lead to hydronephrosis and permanent kidney damage—often symptomless until advanced.
- Fatigue and Low Energy: Chronic pain, inflammation, and anemia from heavy bleeding can cause constant tiredness.
- Emotional Stress and Depression: Anxiety, mood swings, relationship strain, and depression are common due to chronic pain and infertility.
- Rare Risk of Cancer: Long-standing ovarian endometriosis may slightly increase the risk of ovarian cancer, especially after menopause.
- Recurrence After Treatment: Endometriosis can return if not fully removed or if hormonal therapy is discontinued.
- Complications from Repeat Surgeries: Multiple surgeries can reduce ovarian reserve and increase internal scarring risks.
- Reduced Quality of Life: Missed work, intimacy issues, and social withdrawal often occur without timely diagnosis and treatment.
Key takeaway: Early diagnosis and expert surgical management can prevent or minimize these complications and improve quality of life.
How Does Endometriosis Impact Fertility and Pregnancy?
Endometriosis is a leading cause of infertility. It can distort pelvic anatomy, block fallopian tubes, and reduce ovarian reserve, making natural conception difficult. It can also affect IVF success rates if untreated.
- Tubal blockage: Adhesions can block egg and sperm transport
- Ovarian damage: Endometriomas reduce egg quantity and quality
- Inflammation: Affects embryo implantation in the uterus
- IVF outcomes: Untreated severe endometriosis can lower success rates; surgery may improve chances
Tip: Early treatment and fertility-sparing laparoscopic surgery can preserve your chances of pregnancy.
Can Lifestyle and Diet Influence Endometriosis?
While lifestyle changes cannot cure endometriosis, they help reduce inflammation and pain, improve hormonal balance, and support overall well-being.
- Anti-inflammatory diet: Eat omega-3-rich foods (fish, chia), turmeric, leafy greens; avoid red meat, sugar, and processed foods
- Exercise: Regular moderate workouts reduce estrogen dominance and improve pelvic blood flow
- Stress management: Yoga, meditation, and relaxation techniques lower cortisol, which can worsen hormonal imbalance
- Avoid endocrine disruptors: Reduce BPA, plastics, and chemicals in food and skincare products
How to Prevent Long-Term Damage from Endometriosis?
Early detection and proactive management can help prevent severe complications and preserve fertility in women with endometriosis.
- Don’t ignore severe or worsening period pain
- Track your symptoms and menstrual cycles regularly
- Consult a gynecologist early for proper evaluation
- Seek a specialist if pain affects work, relationships, or daily life
- Consider laparoscopy if medical treatments are not effective
Tip: Timely intervention is key to preventing complications like adhesions, infertility, and organ damage.
Advanced 3D Laparoscopic Surgery for Endometriosis
Dr. Dimple Doshi performs endometriosis surgery using the Karl Storz Rubina 4K 3D laparoscopic system, ensuring precision and safety for complex cases.
- Enhanced depth perception and superior visualization of pelvic structures
- Accurate dissection of deep infiltrating endometriosis (DIE)
- Safe removal of ovarian cysts and pelvic adhesions
- Minimal scarring with quicker recovery time
Location: Vardaan Hospital, Goregaon West, Mumbai – delivering world-class endometriosis care close to home.
How Is Laparoscopic Surgery for Endometriosis Performed?
Laparoscopic surgery is the gold standard for treating endometriosis. It involves precise removal of lesions while preserving fertility whenever possible.
- Step 1: Anesthesia & Access: General anesthesia is given, and small incisions are made in the abdomen.
- Step 2: Insertion of Laparoscope: A 3D high-definition camera provides a clear view of pelvic organs.
- Step 3: Mapping the Disease: Surgeons identify all endometriotic lesions, adhesions, and cysts.
- Step 4: Excision: Endometriotic tissue, nodules, and adhesions are removed using precision instruments.
- Step 5: Fertility Preservation: Ovaries and tubes are carefully protected, and nerve-sparing techniques are used.
- Step 6: Recovery: Minimal scarring, shorter hospital stay, and quick return to daily activities.
Advanced Technology: At Vardaan Hospital, Dr. Dimple Doshi uses Karl Storz Rubina 4K 3D technology for unparalleled precision.
When Should You See a Specialist for Endometriosis?
Early consultation with a gynecologist can prevent severe complications. Book an appointment if you experience any of the following:
- Painful periods (dysmenorrhea) or pain during sex
- Difficulty conceiving for 6–12 months despite regular attempts
- Frequent bloating, constipation, or persistent fatigue
- Diagnosed or suspected ovarian cysts
- Suspicion of endometriosis or need for a second opinion
Tip: Timely specialist care improves pain management, preserves fertility, and prevents long-term organ damage.
What Are the Treatment Options for Endometriosis?
Treatment for endometriosis focuses on pain relief, disease control, and preserving fertility. Options include both non-surgical and surgical methods.
Non-Surgical Treatments
- Hormonal therapies: Oral contraceptive pills (OCPs), progestins, GnRH analogs, and antagonists to suppress endometrial growth
- NSAIDs: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for pain relief
- Lifestyle measures: Diet changes, physiotherapy, and pelvic floor relaxation exercises
Surgical Treatments
- 3D laparoscopic excision: Precision removal of endometriotic nodules and fibrotic tissue
- Cystectomy: Safe removal of ovarian endometriomas (chocolate cysts)
- Adhesiolysis: Removal of adhesions to restore pelvic anatomy
- Hysterectomy: Reserved for advanced cases where fertility preservation is not a priority
Expert Approach: Dr. Dimple Doshi uses nerve-sparing and fertility-preserving 3D laparoscopic techniques for optimal outcomes.
How Can You Prevent Endometriosis or Its Recurrence?
While endometriosis cannot always be fully prevented, proactive steps can help reduce risk and manage recurrence after treatment.
Hormonal Regulation
- Use hormonal contraceptives to suppress estrogen cycles
- Avoid estrogen-only therapy if you have a high risk
Anti-inflammatory Diet
- Eat foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, turmeric, and leafy greens
- Limit red meat, processed sugar, and trans fats
Detox Your Lifestyle
- Reduce exposure to plastics, BPA, and endocrine disruptors
- Choose organic and minimally processed foods when possible
Early Evaluation
- Never ignore severe menstrual pain or unusual symptoms
- Schedule timely scans or diagnostic laparoscopy when recommended
Post-Surgery Maintenance
- Follow prescribed hormonal suppression therapy
- Maintain regular follow-ups with your gynecologist
What Is the Recovery Timeline After Laparoscopic Surgery for Endometriosis?
Recovery from laparoscopic surgery is usually quick, but healing fully depends on the extent of surgery and overall health. Here’s what to expect:
- Day 1–2: Mild discomfort, bloating, and shoulder pain (due to CO₂ gas). Start walking gently to prevent clots.
- Day 3–7: Resume light household activities. Pain usually improves significantly with medication.
- Week 2: Most patients can return to work (desk jobs). Avoid strenuous exercise or lifting heavy objects.
- Week 4–6: Full recovery for most women. Resume normal exercise, sexual activity, and daily routine after doctor’s clearance.
Tips for Faster Recovery:
- Eat a fiber-rich diet to avoid constipation
- Stay hydrated and walk daily to improve circulation
- Follow your doctor’s post-op care instructions strictly
- Schedule follow-up visits for early detection of recurrence
Why Choose Dr. Dimple Doshi for Endometriosis Treatment?
Dr. Dimple Doshi is a leading gynecologist and laparoscopic surgeon in Mumbai, specializing in advanced, fertility-preserving endometriosis surgery.
- 27+ years of experience in gynecology and advanced laparoscopy
- Performed over 25,000 successful surgeries
- Successfully treated 1,500+ endometriosis cases
- Expert in nerve-sparing, fertility-preserving laparoscopic surgery
- Uses Karl Storz Rubina 3D 4K laparoscopic system for precision and safety
Medical Code for Endometriosis
ICD-10 Codes for Endometriosis
| ICD-10 Code | Description |
|---|---|
| N80.0 | Endometriosis of uterus |
| N80.1 | Endometriosis of ovary |
| N80.2 | Endometriosis of fallopian tube |
| N80.3 | Endometriosis of pelvic peritoneum |
| N80.4 | Endometriosis of rectovaginal septum and vagina |
| N80.5 | Endometriosis of intestine |
| N80.8 | Other endometriosis |
| N80.9 | Endometriosis, unspecified |
CPT Codes for Endometriosis Diagnosis & Treatment
| CPT Code | Description |
|---|---|
| 49320 | Laparoscopy, diagnostic, with or without collection of specimen(s) |
| 58662 | Laparoscopy, surgical; with fulguration or excision of lesions of ovary, pelvic viscera, or peritoneal surface (primary code for endometriosis treatment) |
| 58660 | Laparoscopy, surgical; with lysis of adhesions (salpingolysis, ovariolysis) |
| 58661 | Laparoscopy, surgical; with removal of adnexal structures (partial or total oophorectomy, if severe case) |
| 58925 | Ovarian cystectomy (if associated with chocolate cyst removal, open approach if conversion) |
| 58570 | Laparoscopic total hysterectomy (for severe, refractory endometriosis with uterine involvement) |
FAQs About Endometriosis
Q1. Can I live normally with endometriosis?
Ans. Yes, with proper treatment and lifestyle changes, many women manage endometriosis symptoms effectively and maintain a normal life.Q2. Will endometriosis go away naturally?
Ans. Endometriosis usually does not go away on its own, but symptoms may improve after menopause or with medical treatment.Q3. What is the best lifestyle for endometriosis?
Ans. A healthy diet, regular exercise, stress management, and adequate sleep can help reduce pain and inflammation associated with endometriosis.Q4. How to stop endometriosis from spreading?
Ans. Medical treatments like hormonal therapy, birth control pills, and minimally invasive surgeries help control disease progression.Q5. How long can a person live with endometriosis?
Ans. Endometriosis is not life-threatening, and with treatment, women can live a full lifespan, though quality of life depends on symptom control.Q6. What does stage 3 endometriosis look like?
Ans. Stage 3 indicates moderate endometriosis with multiple implants and possible ovarian cysts (endometriomas) and adhesions in pelvic organs.Q7. Can endometriosis be treated without surgery?
Ans. Yes, through medication, hormonal therapy, and pain management, but surgery is considered for severe or infertility-related cases.Q8. Does endometriosis affect life expectancy?
Ans. No, it does not reduce life expectancy, but it can impact quality of life due to chronic pain and infertility issues.Q9. How do you remove endometriomas?
Ans. Endometriomas are typically removed through laparoscopic surgery to preserve fertility and reduce pain.Q10. Will endometriosis get worse with age?
Ans. Symptoms may worsen over time if left untreated, especially before menopause, though the severity varies among women.Q11. What are the risks of living with untreated endometriosis?
Ans. Risks include chronic pain, infertility, adhesions, bowel or bladder issues, and rarely, ovarian cancer.Q12. What age does endometriosis usually start?
Ans. Endometriosis often starts during the reproductive years, usually in the late teens to early 30s.Q13. Is endometriosis a high-risk condition?
Ans. While not life-threatening, it can cause severe pain, infertility, and organ damage, making early treatment essential.Q14. Can I get pregnant with endometriosis?
Ans. Yes, many women conceive naturally or with fertility treatments, even with endometriosis, depending on its severity.Q15. How to prevent endometriosis naturally?
Ans. There is no guaranteed prevention, but maintaining hormonal balance with diet, exercise, and reducing stress may help lower risk.Q16. Can endometriosis cause weight gain?
Ans. Indirectly, due to hormonal changes, bloating, and medications, but the condition itself does not directly cause weight gain.Q17. Can stress cause endometriosis?
Ans. Stress does not cause endometriosis but can worsen pain and inflammation, making stress management crucial.Q18. What does endometriosis pain feel like?
Ans. It often feels like intense period cramps, pelvic pain, and pain during intercourse, bowel movements, or urination.Take charge of your health today.
Book your consultation with Dr. Dimple Doshi at
Vardaan Hospital, Goregaon West, Mumbai.


 WhatsApp
WhatsApp +91-9820686823
+91-9820686823 Book Appointment
Book Appointment