Advanced Cervical Polyp Diagnosis & Treatment in Goregaon West, Mumbai
Dr. Dimple Doshi (MBBS, MD, DGO)
Lady Gynecologist & Laparoscopic Surgeon
27+ years’ experience
20,000+ surgeries completed
Introduction
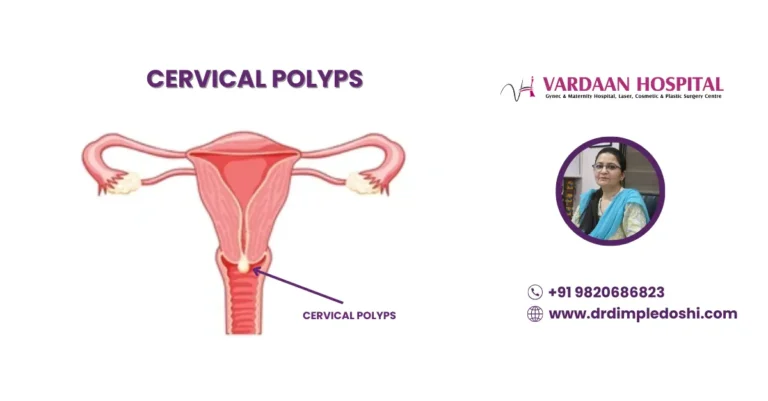
Cervical Polyps are basically lumps that appear on the cervical canal—the passage that connects to the uterus. They can be grey, red, or purple and come in various shapes like fingers, bulbs, or thin stems. These polyps range in size from a few millimeters to several centimeters. Most cervical polyps are non-cancerous, with only 0.2% to 1.5% having the potential to become cancerous, which is very rare.
Dr. Dimple Doshi, an experienced gynecologist at Vardaan Hospital, Goregaon West, Mumbai, specializes in the accurate diagnosis and treatment of cervical polyps. With a focus on prevention and holistic care, Dr. Doshi provides personalized consultations that include both treatment and preventive advice.
Incidence of Cervical Polyps
Cervical polyps are relatively common and usually occur in women over the age of 20, especially those who have given birth multiple times. They are rarely seen in young girls who have just begun menstruating.
What Causes Cervical Polyps?
The causes may include:
- Infections in the cervical canal
- Persistent inflammation
- Hormonal imbalances, especially estrogen sensitivity
- Blocked blood vessels near the cervix
- Exposure to estrogen-like chemicals such as phthalates
Types of Cervical Polyps
Based on their origin, cervical polyps are categorized into:
- Endocervical Polyps: Originate from cervical glands inside the endocervix.
- Ectocervical Polyps: Originate from the outer surface of the cervix (ectocervix).
Symptoms of Cervical Polyps
Common symptoms include:
- Unusually heavy vaginal bleeding
- Spotting or bleeding after sexual intercourse
- Bleeding after menopause
- Bleeding between menstrual cycles
- Vaginal discharge, possibly foul-smelling due to infection
How Are Cervical Polyps Diagnosed?
A gynecologist can detect cervical polyps during a routine pelvic exam. A biopsy may be performed by taking a small tissue sample, which is sent to a lab to determine if the cells are benign or have abnormalities that could indicate cancer.
What Are the Treatment Options for Cervical Polyps?
If symptoms occur, treatment becomes necessary. Options include:
- Gently removing the polyp from its base
- Using a surgical string to tie the polyp and then cutting it off
Post-treatment side effects may include:
- Mild pain
- Cramps
- Light vaginal bleeding or spotting
How Can Cervical Polyps Be Prevented?
While cervical polyps can’t always be prevented, you can reduce the risk by:
- Taking medications to control infections
- Attending regular pelvic and gynecological examinations
Who is the Best Doctor for Cervical Polyps Treatment in Goregaon West?
Dr. Dimple Doshi is a highly experienced and trusted gynecologist in Goregaon West, Mumbai. With her extensive experience and patient-centric approach, she is considered one of the best doctors for cervical polyp treatment in the region.
Which is the Best Hospital for Cervical Polyps Treatment in Goregaon West?
Vardaan Hospital, Goregaon West, is equipped with state-of-the-art facilities and experienced medical staff. It is recognized for its advanced gynecological treatments and is the preferred choice for cervical polyps treatment.
What is the Cost of Cervical Polyps Treatment in Mumbai?
The cost of cervical polyps treatment in Mumbai generally ranges from ₹3,000 to ₹10,000, depending on the complexity of the case, diagnostic tests required, and the method of removal. Consult Dr. Dimple Doshi for an accurate estimate after clinical evaluation.
Medical Code for Cervical Polyps
ICD-10 Code:
- N84.1 – Polyp of cervix uteri
CPT Codes:
- 57500: Cervical biopsy or excision
- 57505: Endocervical curettage
- 58100: Endometrial biopsy (with/without cervical sampling)
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1. What are cervical polyps, and are they dangerous?
Ans. Cervical polyps are small growths on the cervix that are usually benign. Only a small percentage have the potential to become cancerous.
Q2. What causes cervical polyps?
Ans. They may be caused by hormonal changes, infections, inflammation, or blood vessel issues near the cervix.
Q3. What are the signs I might have cervical polyps?
Ans. Symptoms include abnormal vaginal bleeding, spotting after sex, post-menopausal bleeding, and unusual vaginal discharge.
Q4. Can cervical polyps go away on their own?
Ans. Some small polyps may fall off on their own, but symptomatic ones generally require removal.
Q5. How are cervical polyps removed?
Ans. They can be removed manually or via minor surgical procedures using strings or instruments.
Q6. Is the removal of cervical polyps painful?
Ans. The procedure is usually quick and causes minimal discomfort. Some women may feel light cramps or spotting afterward.
Q7. How can I prevent cervical polyps?
Ans. You can lower your risk by treating infections early and getting regular gynecological exams.
Q8. Is cervical polyp treatment covered under insurance?
Ans. Most health insurance plans cover minor gynecological procedures, including cervical polyp removal. It’s best to confirm with your provider.
