Specialized Treatment for Cervical Erosion in Goregaon West, Mumbai
Cervical erosion ranks as one of the most commonly found gynecological conditions. It affects 17 to 50% of the young population; the incidence might reach as high as 80% among sexually active adolescents. The prevalence decreases in individuals age 35 and above.
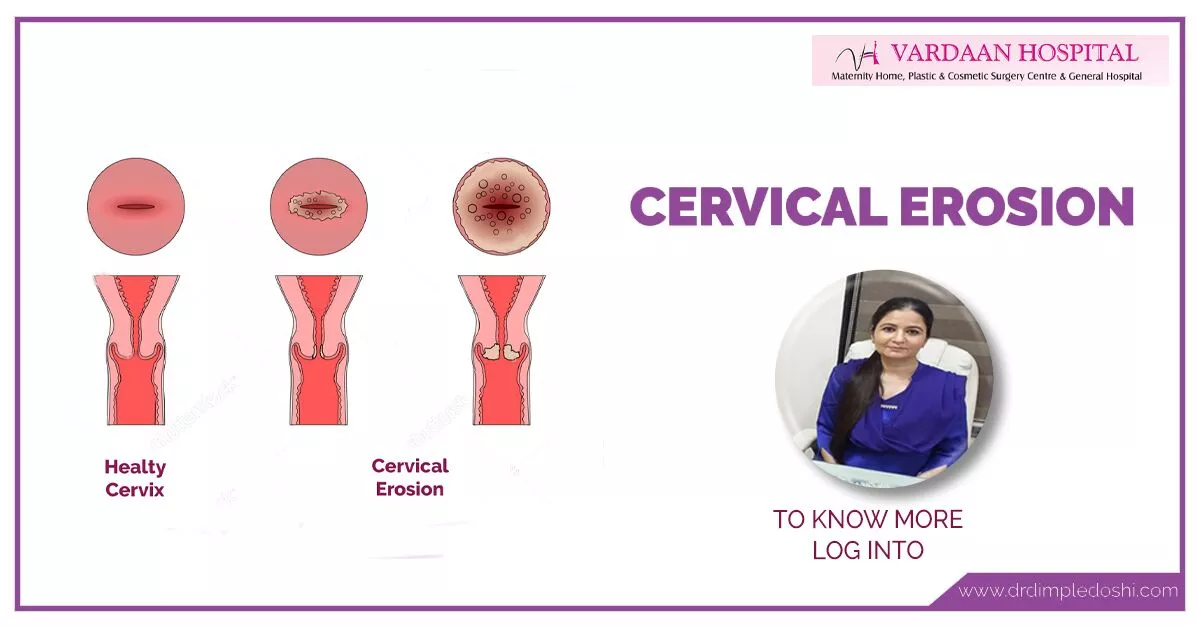
When glandular cells from inside the cervical canal grow onto the outside of the cervix, cervical erosion occurs. These glandular cells, which are red, make the area appear red.
Cervical erosion is sometimes called cervical ectropion or cervical ectopy.
ICD-10 Codes for Cervical Erosion:
Cervical erosion, also known as cervical ectropion, refers to a condition where the cells from the inside of the cervix spread to the outside. The relevant ICD-10 codes are:
- N87.0: Cervical erosion (mild dysplasia)
- N87.1: Moderate dysplasia of the cervix (cervical erosion that has progressed)
- N87.9: Cervical dysplasia, unspecified (if the erosion is not further specified)
CPT Codes for Treatment of Cervical Erosion:
Treatment of cervical erosion may involve various procedures, including diagnostic and therapeutic interventions:
- 57500: Biopsy of cervix, single or multiple, or local excision of lesion, with or without fulguration (commonly used for diagnostic and treatment purposes)
- 57505: Endocervical curettage (for obtaining a sample from the cervix for diagnostic purposes)
- 57460: Colposcopy of the cervix including upper/adjacent vagina; with loop electrode biopsy(s) of the cervix (if a more detailed examination and treatment are needed)
- 57288: Fulguration (electrocautery) or cryotherapy (destruction of abnormal cervical tissue)
Dr. Dimple Doshi at Vardaan Hospital; believes prevention is better than cure, and thus apart from the precise treatment guidelines; preventive measures are an essential part of our consultations with the patients who have either had it or want to know more about it.
Cervical Ectropion Facts
- It is common.
- It is not linked to cervical cancer.
- It often goes away on its own.
- It may not cause any symptoms. In fact, some women are born with it.
- Treatment is required if it is causing symptoms, such as white discharge or light bleeding during or after sex.
Importance of cervical ectropion
Although cervical ectropion resolves itself over time, it creates a vulnerable ground for seeding various sexually transmitted infections including Chlamydia, gonorrheal, HIV or HPV infections as the glandular epithelium can easily take up the STDs. Cervical erosion may be debilitating for females who experience excessive vaginal discharge or frequent vaginal bleeding. However, appropriate treatment is successful in relieving these symptoms.
cervical ectropion does not lead to infertility; neither does it has any adverse effects on pregnancy or the fetus.
How do you Develop Cervical Erosion?
A lot of women are born with cervical erosion. It can also be caused if you are:
- Young; as cervical erosion disappears in aged women.
- Attaining puberty
- pregnant
- Taking the combined hormonal pills like contraceptive pills.
What is symptoms of Cervical Erosion?
Most of the time, cervical erosion does not cause any symptoms and disappears on its own.
But it may be responsible for symptoms like:
- Easy bleeding
- profuse white discharge
- Light bleeding, spotting, pain or discharge during or after sex.
- Bleeding or pain during or after examination by your gynecologist.
- Intermenstrual spotting or bleeding or bleeding between regular periods
- Spotting after exercise
How to Diagnose Cervical Ectropion?
Many times you may not know that you are having cervical erosion until you visit your gynecologist for symptoms like
White discharge Spotting, discharge and pain after sex Intermenstrual bleeding.
Or
It may be diagnosed incidentally when you go to your gynecologist for a normal check-up or pap smear examination.
Treatment Options for Cervical Ectropion
- Cautery: An outpatient procedure; of 2 types:
- Electrocautery Cautery probe is held for 30 sec against the area of erosion to destroy the abnormal cells.
- Cryotherapy Cautery probe is held until the tissue is frozen; best suited for infertile patients or in pregnancy.
- Microwave tissue coagulation
- Co2 laser ablation
- Vaginal suppositories containing interferon; polydeoxyribonuclotide; boric acid and phenoxyethanol triticum vulgare extract
- PRP application
- Silver nitrate application
- Focused ultrasound
Out of all these; cautery is said to be 92 to 95 % effective in treating cervical erosion
Diathermy or Cautery for Treatment of Cervical Erosion
It is the most commonly used method used by gynecologists’ to treat cervical erosion.
How is Diathermy or Cauterisation of Cervical Ectropion Performed?
Diathermy or cauterisation of cervical ectropion is usually done under local anaesthesia and you may be given short general anaesthesia if you wish so..
- You will be placed on a couch with your legs supported.
- After applying numbing lubricant at the introitus; an instrument called a speculum is inserted in the vagina so that your cervix can clearly be seen.
- The diathermy procedure is maybe done under colposcopy guidance and usually takes about 5 – 10 minutes. You will be given a local anesthetic so you will be awake, but you should not feel any pain. The local anesthetic will sting a little, but the area will very quickly go numb. The local anesthetic may also increase your heart rate. The side effects of the local anesthetic will only last briefly and should not cause you any harm.
- After local anesthesia; cautery probe is held against the affected area until all the cells seem to be completely destroyed.
Post-Operative Care
You will be able to go home 15 minutes after the treatment if you feel comfortable. You can drive a car or take public transport.
It is normal to experience watery discharge; spotting or bleeding or cramping lower abdominal pain for the first few days.
The discharge should not be yellow or foul smelling. If this occurs, you must see your doctor who will start antibiotics.
For 4 weeks after the procedure you should
- Use sanitary towels and not tampons.
- Avoid sexual intercourse.
- Avoid swimming.
- Avoid vaginal creams.
Recurrence and Prevention of Cervical Erosion
Properly treated cervical erosion does not return in absence of major hormonal changes in your body.
Cervical erosion is partly preventable by avoiding exogenous hormones like contraceptives or hormone replacement therapy.

