Effective Bartholin Cyst Solutions in Goregaon West, Mumbai
Bartholin Cyst
Introduction
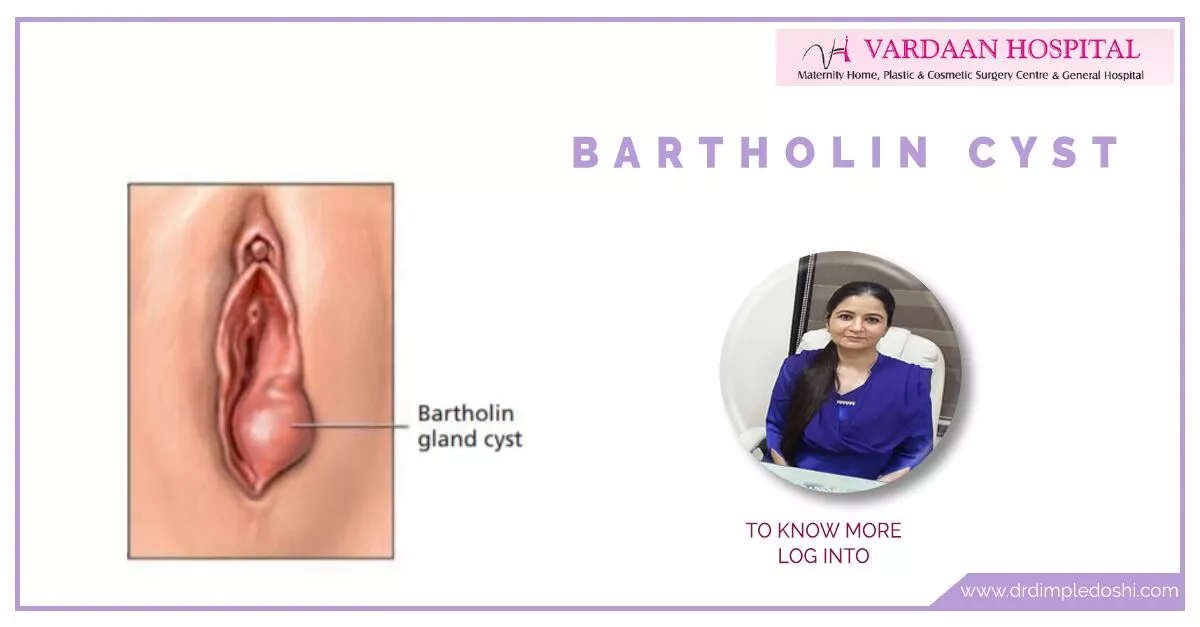
Bartholin’s glands are located on each side of the vaginal opening. Main function of these glands is secretion of sticky fluid that lubricates the lower end of vagina during sexual intercourse. These glands become active when a girl reaches maturity and they are not felt; but when they enlarge; they form either Bartholin cyst or abscess.
Bartholin cyst develops when the openings of these glands become blocked so the fluid goes back to collect inside and enlarge the gland; this is called Bartholin cyst. And when this cyst becomes infected; pus gets trapped inside; and this is called a Bartholin abscess.
Bartholin’s cysts affect about 2% of women at some point in their life. They most commonly occur during childbearing years.
ICD-10 Codes for Bartholin’s Cyst:
A Bartholin’s cyst is a fluid-filled sac that forms in the Bartholin’s gland, located near the vaginal opening.
- N84.1: Polyp of cervix uteri (sometimes used if the cyst is mistaken for or associated with a cervical polyp, but less specific)
- N83.20: Unspecified ovarian cyst (sometimes used for cystic masses in the pelvic area, though not specific for Bartholin’s cysts)
- N84.3: Other cysts of the vulva (this is a more appropriate code for Bartholin’s cysts)
CPT Codes for Treatment of Bartholin’s Cyst:
Treatment typically involves drainage or removal of the cyst. Common CPT codes include:
- 56405: Incision and drainage of Bartholin’s gland cyst (for removing the fluid and providing symptomatic relief)
- 56420: Marsupialization of Bartholin’s gland cyst (a procedure where the cyst is surgically opened and its edges are sutured to create a permanent pouch, preventing reformation)
Dr. Dimple Doshi at Vardaan Hospital; believes prevention is better than cure, and thus apart from the precise treatment guidelines; preventive measures are an essential part of our consultations with the patients who have either had it or want to know more about it.
- Sometimes Bartholin’s cyst develops without reasons due to blockage of its opening.
- Infection of the gland opening may happen by bacteria like E. Coli; or can happen by sexually transmitted infections like gonorrhoea or chlamydia.
Small Bartholin s cyst may not get noticed; if the cyst grows; it may be felt. The common symptoms are:
- Lump near the vaginal opening; and may be painful if it develops infection.
- Discomfort while walking or sitting
- Pain during sexual intercourse.
- Fever.
Conservative Treatment
Sitz bath can make the cyst burst and drain on its own.
- Fill a tub enough to cover the vulva and gently sit
- Do this several times a day for 3 to 4 days.
Surgical Treatment
- Surgical drainage and marsupialisation: Here your gynaecologist will drain the cyst of its contents after putting a small cut ;draining all its contents and then the edges of the cyst wall are stitched to the skin to form a small pouch. The area is packed with a small gauze piece soaked in antiseptic solution and kept there for 24 hours.This procedure takes hardly half an hour; done under sedation and you can be discharged on the same day. This is the standard method to prevent recurrence.
- Surgical drainage only: In this method the contents of the cyst are drained after putting a cut on it and a small catheter is kept for 6 weeks to allow the cyst to drain completely. This is less used in modern times.
- Removing the gland: This option is considered only there is recurrences which bother you and force you to go for the surgical treatments again and again.
- Recurrence
- Infection and sepsis
- Safer sex practices — like using condoms
- Good hygiene habits may help to prevent infection of a cyst and the formation of an abscess.
These measures can help prevent the development and recurrences of Bartholin cyst to some extent.
