Advanced Dermoid Cyst Treatment in Goregaon West, Mumbai
Dermoid Cyst
Introduction
Dermoid cysts are a very different type of usually benign tumors found in the ovary; also found in the brain; sinuses or spinal cord. Dermoid cysts; also known as mature cystic teratomas; have a reported prevalence of about 20%. And in 10 to 15% of cases, they occur in both ovaries.
ICD-10 Codes for Dermoid Cyst:
A dermoid cyst, also known as a mature cystic teratoma, is a type of ovarian cyst that contains various types of tissues. The relevant ICD-10 codes are:
- D27.0: Benign neoplasm of the ovary (for benign dermoid cysts)
- N83.20: Unspecified ovarian cyst (if the specific type of cyst is not detailed)
CPT Codes for Treatment of Dermoid Cyst:
Treatment of dermoid cysts often involves surgical procedures. Common CPT codes include:
- 58662: Laparoscopy, surgical; with fulguration or excision of lesions of the ovary, pelvic viscera, or peritoneal surface (e.g., removal of dermoid cysts)
- 58720: Salpingo-oophorectomy, complete or partial, unilateral or bilateral (if removal of the affected ovary is necessary)
- 58150: Total abdominal hysterectomy (corpus and cervix), with or without removal of tube(s) and/or ovary(s) (when the cyst is part of a more extensive surgical procedure)
Dr. Dimple Doshi at Vardaan Hospital; believes prevention is better than cure, and thus apart from the precise treatment guidelines; preventive measures are an essential part of our consultations with the patients who have either had it or want to know more about it.
What are Dermoid Cysts
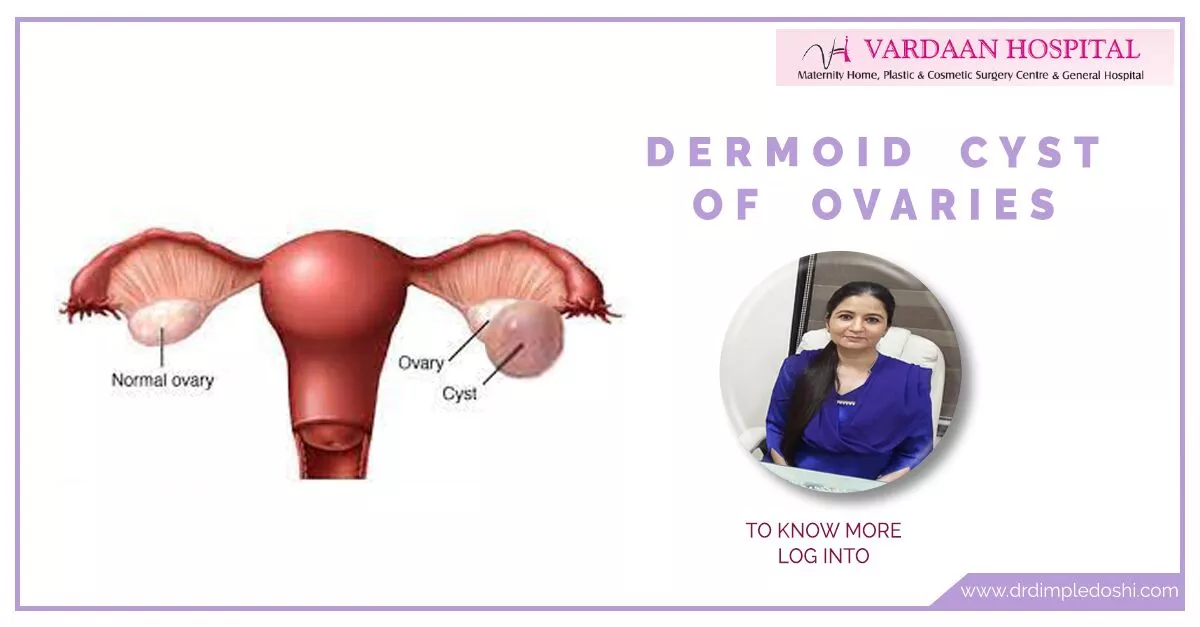
Dermoid cyst in the ovary is a sac-like structure that may contain hair, teeth, bone, cartilage, fatty fluids, some oily waxy substances; thyroid tissues, etc. These dermoid cysts grow slowly and do not cause any symptoms until they rupture or get twisted. Dermoid cysts range from half an inch to 45 cm in size
Causes of Dermoid Cysts
Dermoid cysts are caused by the entrapment of skin and skin structures in the tissues where they can grow. For example; ovaries; skull; spinal cord; sinuses etc. So it means that they are present since birth. They may be small in size initially but they can grow to become very big. And as their cells are similar to outer skin; they contain bone; hair; teeth sebum etc.
There is probably some genetic predisposition in first-degree relatives.
Common symptoms are:
- Abdominal or lower back pain
- Pain during sexual intercourse
- Nausea with or without vomiting
- Urinary problems due to a big dermoid pressing on the urinary bladder.
- Abnormal vaginal bleeding.
- Abdominal distension and bloatedness.
You have to seek immediate attention if there is
- Sudden abdominal pain
- Vomiting
These symptoms indicate either rupture or twisting of the cyst inside the abdomen. Both are serious medical emergencies. Because if the twisting of the dermoid cyst is not corrected on time; the ovary can develop gangrene and may require removal. And if it ruptures inside the abdomen; it can lead to sepsis and shock.
Treatment of Dermoid Cyst
The treatment of dermoid cyst of ovary is surgery .
It can be done either by laparotomy or laparoscopy
Laparoscopy is the method of choice for removal of dermoid cyst of the ovary. Laparoscopy involves using a slender telescope inserted through the belly button. Dermoid cyst is extracted out through key holes. It involves faster recovery and better cosmetic outcome.
What are the Chances of Dermoid Cyst of Ovary Turning into Cancer
Most of the dermoid cysts in the ovaries are detected in the younger and reproductive age groups; and the large majority ; about 98% are benign; about 2% become malignant. The risk factors are:
- High Ca125 levels
- Old age
- Long standing dermoid cysts
- Large tumor masses
- Postmenopausal status
Any long-standing dermoid cyst of the ovary has a thin chance of turning into a cancerous tumor. So if diagnosed in early years; the surgery should not be delayed.
Dr Dimple Doshi ; at Vardaan hospital aims to carry out the surgery for dermoid cyst in such a way that we can serve the maximum normal ovary without disturbing its blood supply while removing the cyst.

